
Date: 2024-10-19 Page is: DBtxt003.php txt00007287
SECTOR / ENVIRONMENT
AGRICULTURE (DAIRY) / WATER
It Takes HOW Much Water to Make Greek Yogurt?! ... Dairy products require a whole lot of water—and many of them come from drought-ridden California.
AGRICULTURE (DAIRY) / WATER
It Takes HOW Much Water to Make Greek Yogurt?! ... Dairy products require a whole lot of water—and many of them come from drought-ridden California.

http://www.motherjones.com/environment/2014/03/california-water-suck
Burgess COMMENTARY
These graphics came as something of a surprise to me. I know water is important, but I had no idea hos much (potable) water is embedded in the many products of the dairy industry.
I have worked in parts of the world where there was drought, and became very aware how important potable water is for the life of vegetation, animals and people. It seems that parts of the USA are becoming more susceptible to drought conditions including California which is host to a huge part of the US dairy industry and other water consuming segments of agriculture.
It should be of great concern that much of the agriculture in Ca;lifornia is using 'fossil' water from aquifers to supplement the currently available rainfall and snowmelt. This is unsustainable ... but not getting the attention it deserves. (Commentary added December 2021)
Peter Burgess
By Julia Lurie and Alex Park
Mon Mar. 10, 2014 3:00 AM PDT

California is experiencing one of its driest years in the past half millennium. It also happens to also be the country's leading dairy supplier. With profits surpassing $7 billion in 2012, the California dairy industry is far and away the most valuable sector of the state's enormous agricultural bounty. Unfortunately, as the chart above shows, dairy products use a whole lot of water.
Why is our dairy so thirsty? According to a 2012 study in the journal Ecosystems by Mesfin Mekonnen and Arjen Hoekstra, 98 percent of milk's water footprint comes from cows' food.
Now, cattle eat all sorts of things, but a dairy cow's diet in the United States consists primarily of alfalfa hay, grass hay, corn, and other grains like soy or canola. Alfalfa hay is a superfood of sorts for dairy cows—it's high in protein, high in energy, and it's digestible. 'When you feed alfalfa, you produce more milk,' says Dan Putnam, a plant scientist at the University of California-Davis. 'That's the bottom line.' In a University of California alfalfa blog (yes, that exists), Putnam and his colleague wrote, 'The next time you have pizza (with cheese), milk on your cereal, or ice cream, thank alfalfa.'
Putnam used a University of Wisconsin study to estimate the amount of milk an acre of alfalfa hay can to produce in a year. If you consider Putnam's calculations and the California Department of Water Resources' statistics on the yield of an acre of alfalfa, the water footprint of a gallon of milk looks something like this:
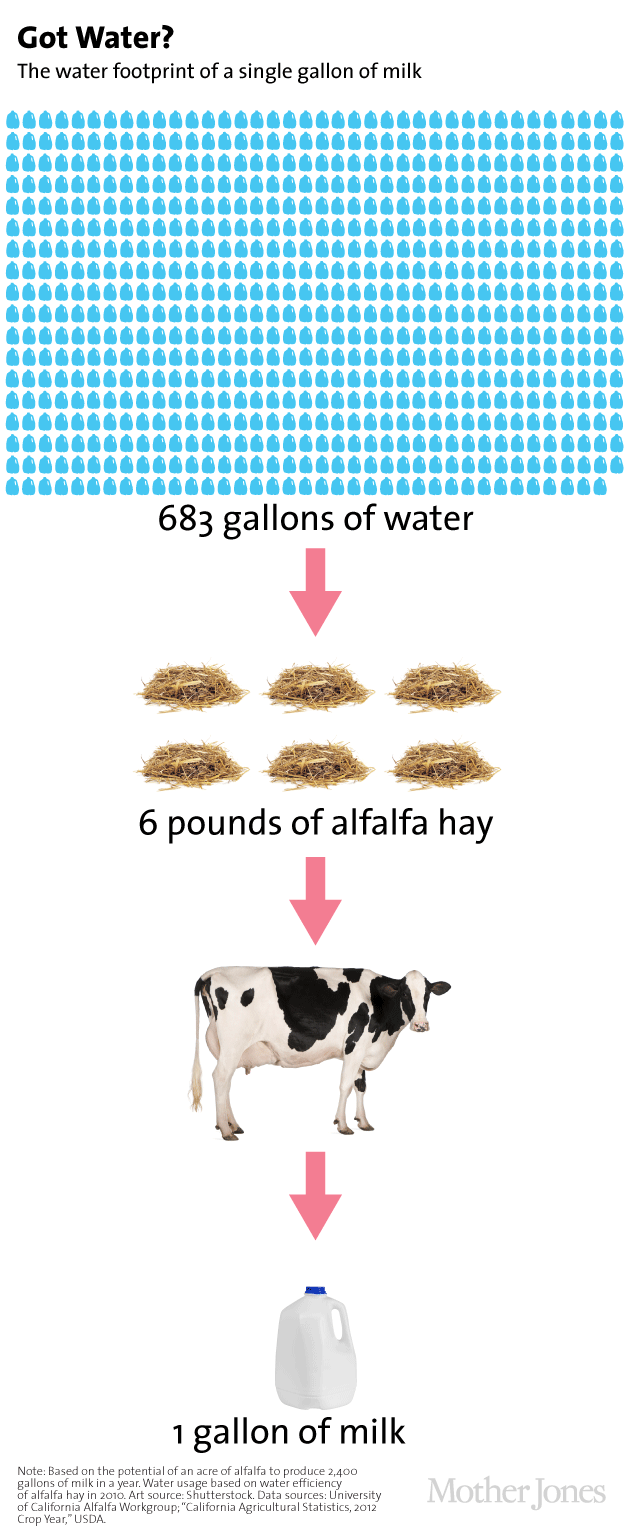
Given the size of the state's dairy industry, it may come as no surprise that, as of 2010, alfalfa led the state's crops in total water consumption and was a close second in total irrigated crop area. Here are some of the other top water users:
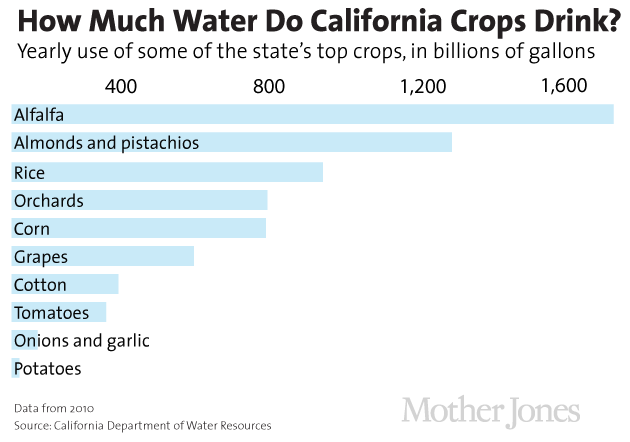
The vast majority of alfalfa grown in California is fed to California's cows, but as the New York Times recently reported, some of the state's alfalfa hay—Putnam estimates about 10 percent—is shipped abroad, where farmers can reap higher profits.
Unfortunately, the water footprint of meat products is even bigger than that of dairy. According to another study by Mekonnen and Hoekstra, it takes a total of 425 gallons of water to produce a four-ounce serving of beef in the United States. The same size serving of pork takes 165 gallons of water; for chicken, 66 gallons.
The same New York Times piece suggests that replacing half of the animal products in your diet with plant-based substitutes reduces your food-related water footprint by 30 percent. Going vegetarian reduces it by 60 percent.
JULIA LURIE Editorial Fellow ... Julia Lurie is a Mother Jones editorial fellow. She can be reached at jlurie@motherjones.com
ALEX PARK Editorial Fellow ... Alex Park is an editorial fellow at Mother Jones.