
Date: 2025-10-17 Page is: DBtxt003.php txt00013026
Famine 2017
Nigeria / Somalia / South Sudan / Yemen
WorldViews Analysis ... Starving to death ... Wars in four countries have left 20 million people on the brink
Burgess COMMENTARY
Peter Burgess
WorldViews Analysis
Starving to death
Wars in four countries have left 20 million people on the brink
Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on Google Plus
Share via Email
Share on LinkedIn
Share on Pinterest
Share on Tumblr
Print Article
Comments
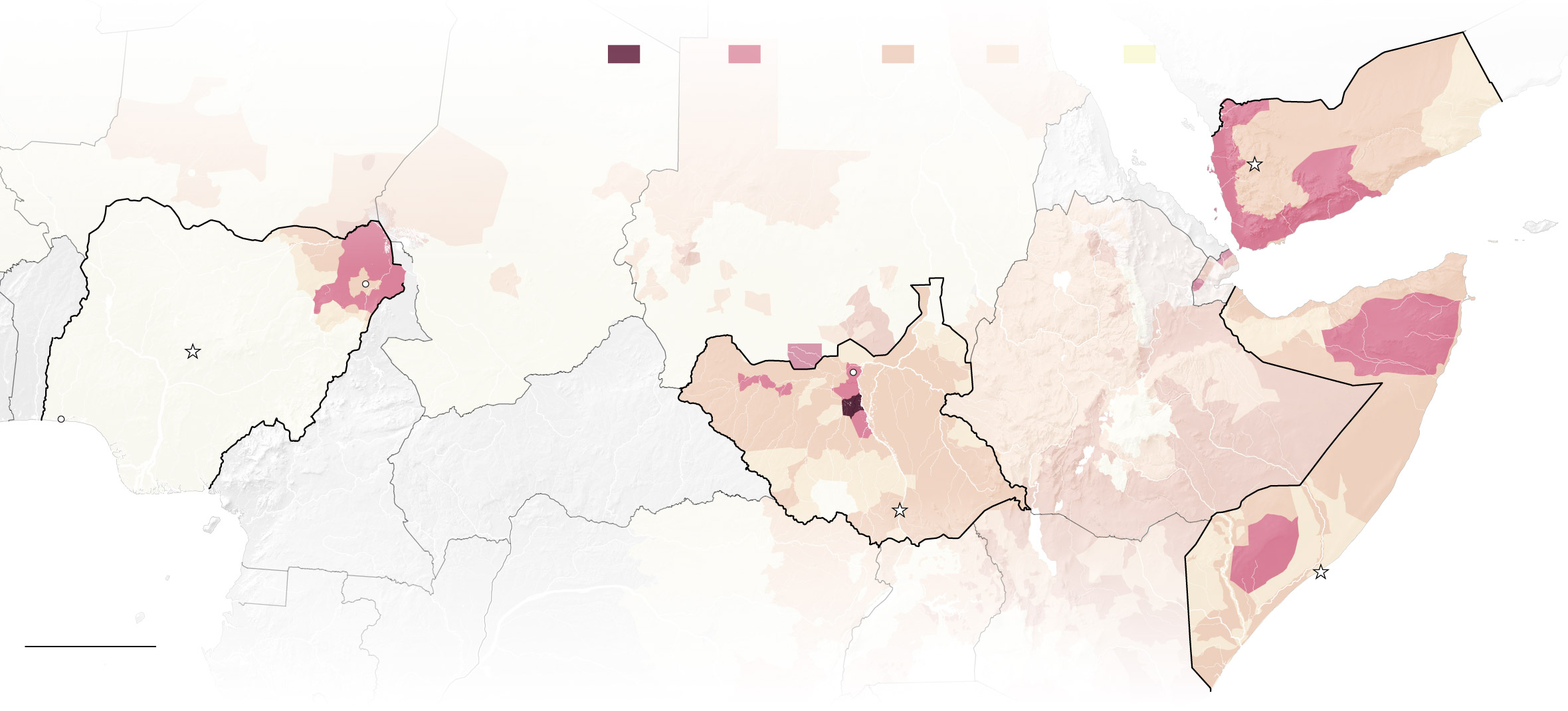 Food insecurity conditions:
Famine
Emergency
Crisis
Stressed
Minimal
MALI
YEMEN
Red
Sea
NIGER
7.3 million
ERITREA
Sanaa
SUDAN
CHAD
NIGERIA
DJIBOUTI
Maiduguri
5.1 million
people at risk
Abuja
Bentiu
ETHIOPIA
Lagos
SOUTH SUDAN
SOMALIA
CENT. AFRICAN REP.
5 million
2.9 million
people at risk
CAMEROON
Juba
Atlantic
Ocean
Mogadishu
CONGO
UGANDA
KENYA
Indian
Ocean
300 MILES
Our world produces enough food to feed all its inhabitants. When one region is suffering severe hunger, global humanitarian institutions, though often cash-strapped, are theoretically capable of transporting food and averting catastrophe.
But this year, South Sudan slipped into famine, and Nigeria, Somalia and Yemen are each on the verge of their own. Famine now threatens 20 million people — more than at any time since World War II. As defined by the United Nations, famine occurs when a region’s daily hunger-related death rate exceeds 2 per 10,000 people.
The persistence of such severe hunger, even in inhospitable climates, would be almost unthinkable without war.
Each of these four countries is in a protracted conflict. While humanitarian assistance can save lives in the immediate term, none of the food crises can be solved in the long term without a semblance of peace. The threat of violence can limit or prohibit aid workers’ access to affected regions, and in some cases, starvation may be a deliberate war tactic.
Entire generations are at risk of lasting damage stemming from the vicious cycle of greed, hate, hunger and violence that produces these famines. Children are always the most affected, as even those who survive may be mentally and physically stunted for life. And while this article focuses on the four countries most immediately at risk, ongoing conflicts in Congo, the Central African Republic, Libya, Iraq, Syria and Afghanistan has left millions hungry in those places, too.
Food insecurity conditions:
Famine
Emergency
Crisis
Stressed
Minimal
MALI
YEMEN
Red
Sea
NIGER
7.3 million
ERITREA
Sanaa
SUDAN
CHAD
NIGERIA
DJIBOUTI
Maiduguri
5.1 million
people at risk
Abuja
Bentiu
ETHIOPIA
Lagos
SOUTH SUDAN
SOMALIA
CENT. AFRICAN REP.
5 million
2.9 million
people at risk
CAMEROON
Juba
Atlantic
Ocean
Mogadishu
CONGO
UGANDA
KENYA
Indian
Ocean
300 MILES
Our world produces enough food to feed all its inhabitants. When one region is suffering severe hunger, global humanitarian institutions, though often cash-strapped, are theoretically capable of transporting food and averting catastrophe.
But this year, South Sudan slipped into famine, and Nigeria, Somalia and Yemen are each on the verge of their own. Famine now threatens 20 million people — more than at any time since World War II. As defined by the United Nations, famine occurs when a region’s daily hunger-related death rate exceeds 2 per 10,000 people.
The persistence of such severe hunger, even in inhospitable climates, would be almost unthinkable without war.
Each of these four countries is in a protracted conflict. While humanitarian assistance can save lives in the immediate term, none of the food crises can be solved in the long term without a semblance of peace. The threat of violence can limit or prohibit aid workers’ access to affected regions, and in some cases, starvation may be a deliberate war tactic.
Entire generations are at risk of lasting damage stemming from the vicious cycle of greed, hate, hunger and violence that produces these famines. Children are always the most affected, as even those who survive may be mentally and physically stunted for life. And while this article focuses on the four countries most immediately at risk, ongoing conflicts in Congo, the Central African Republic, Libya, Iraq, Syria and Afghanistan has left millions hungry in those places, too.
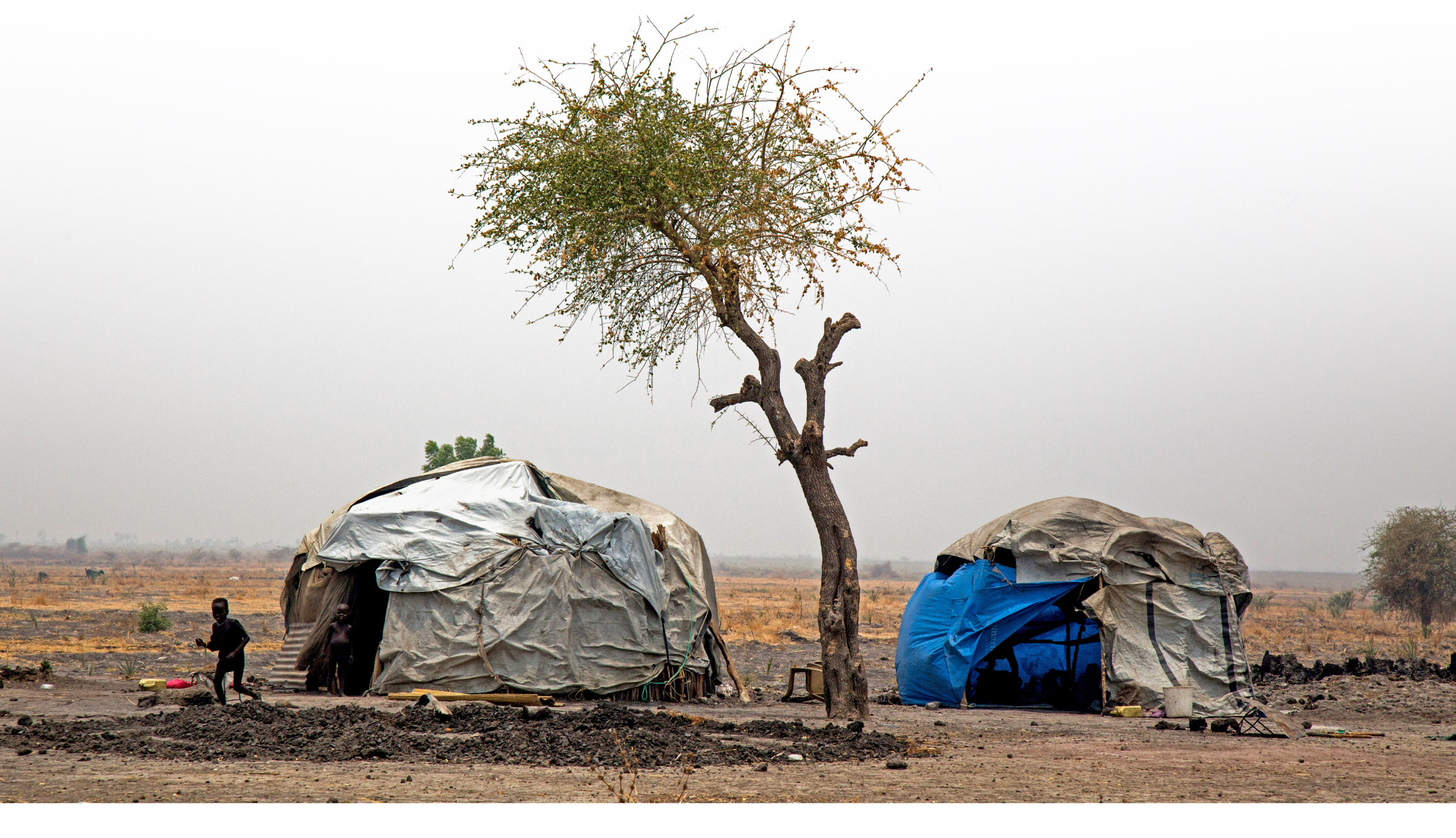 War and famine along the White Nile, in South Sudan
Two children walk out from their shelter in Dablual in Mayendit on March 23, 2017. Hundreds of people have recently fled Dablual, still under control of the opposition troops, due to the ongoing fighting and food crisis.
(Albert Gonzalez Farran for The Washington Post)
In February, the United Nations declared a famine in South Sudan’s Mayendit and Leer counties. It was the world’s first famine declaration since 2011, in Somalia.
But even in these two counties, more people still die every day from bullets than from empty stomachs or disease. The state the counties are in, Unity, has seen some of the most ruthless violence since South Sudan became an independent country five years ago.
Unity is the home state of Riek Machar, former vice president and leader of a rebel army of mostly ethnic Nuer people that has been locked in violent confrontations with South Sudan’s army, controlled by President Salva Kiir of the Dinka ethnic group, since 2013. Kiir’s army and allied militias have swept through Unity time and again, razing and burning entire villages, slaughtering and raping as they go. Thousands of people have drowned in the state’s rivers and swamps as they fled.
Those rivers and swamps would otherwise provide Unity’s people with abundant fish and water for irrigation. But relentless war renders just about all aspects of daily life unsafe, with people too afraid to leave home, fish, plant or trade. Even fleeing can be risky. Many are eating grass and water lilies just to survive.
War and famine along the White Nile, in South Sudan
Two children walk out from their shelter in Dablual in Mayendit on March 23, 2017. Hundreds of people have recently fled Dablual, still under control of the opposition troops, due to the ongoing fighting and food crisis.
(Albert Gonzalez Farran for The Washington Post)
In February, the United Nations declared a famine in South Sudan’s Mayendit and Leer counties. It was the world’s first famine declaration since 2011, in Somalia.
But even in these two counties, more people still die every day from bullets than from empty stomachs or disease. The state the counties are in, Unity, has seen some of the most ruthless violence since South Sudan became an independent country five years ago.
Unity is the home state of Riek Machar, former vice president and leader of a rebel army of mostly ethnic Nuer people that has been locked in violent confrontations with South Sudan’s army, controlled by President Salva Kiir of the Dinka ethnic group, since 2013. Kiir’s army and allied militias have swept through Unity time and again, razing and burning entire villages, slaughtering and raping as they go. Thousands of people have drowned in the state’s rivers and swamps as they fled.
Those rivers and swamps would otherwise provide Unity’s people with abundant fish and water for irrigation. But relentless war renders just about all aspects of daily life unsafe, with people too afraid to leave home, fish, plant or trade. Even fleeing can be risky. Many are eating grass and water lilies just to survive.
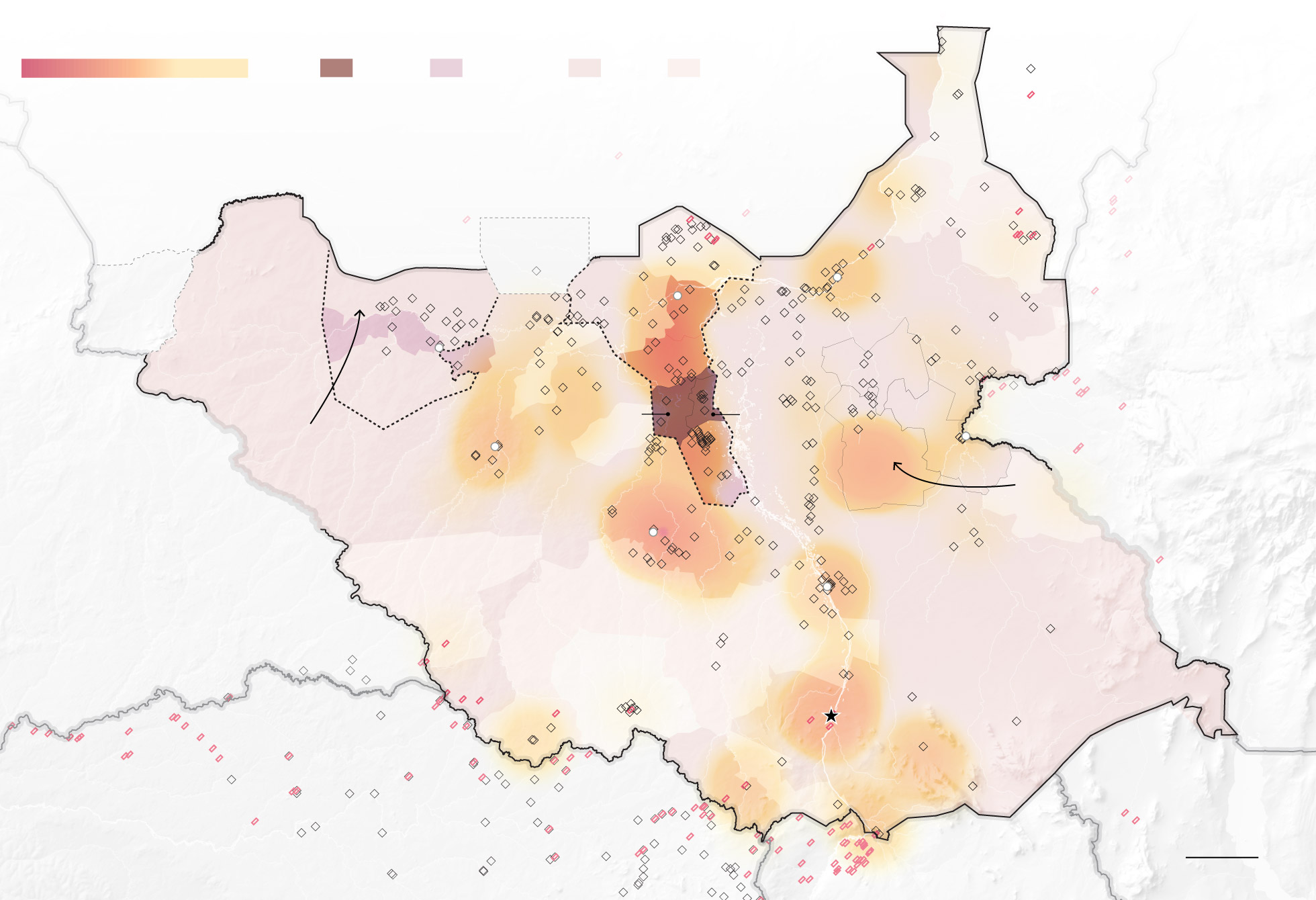 Conflict zone
Food insecurity
Forced migration
Heavy
Less
Famine
Emergency
Crisis
Stressed
Internally displaced camps
Refugee camps
White
Nile
SUDAN
ABYEI
Disputed
Malakal
KAFIA
KINDI
Bentiu
Disputed
UNITY
ETHIOPIA
Aweil
Nyirol
Mayendit Co.
Leer Co.
Akobo
Famine
An estimated 53,880 people have migrated to Sudan this year, many from Northern Bahr el Ghazal, because they have little access to food.
Famine
Wau
Uror
Akobo
Fighting in Uror County between government troops and armed opposition in mid-February displaced an estimated 13,000 to Akobo and Nyirol counties.
Rumbek
CENTRAL
AFRICAN
REP.
Bor
SOUTH SUDAN
Juba
Mountain
Nile
KENYA
CONGO
Attacks between 2014-2017 were used to map the conflict zones.
UGANDA
50 MILES
Both the rebels and the government have made it difficult for aid workers to reach the most-affected counties. The Washington Post’s Africa correspondent, Kevin Sieff, recently reported on the government’s obstructionism.
“Some of their actions appear to be brute thuggery, like the theft by soldiers last summer of more than 4,000 tons of food from a warehouse in Juba, the capital, enough to feed 220,000 people for a month,” he wrote. “But aid workers fear the government is intentionally denying aid to regions where it believes residents support the rebels.”
Sieff described how, at more than 70 checkpoints on the road between Juba and Unity State, soldiers would often demand bribes or food from aid workers, and how the government refuses to let the United Nations operate flights that could drop food aid over areas at risk of famine. Dozens of aid workers attempting workarounds have been killed in the war’s crossfire.
The United States and others in the U.N. Security Council have proposed an arms embargo to limit the South Sudan government’s capacity for violence. But when it came to a vote last December, more than half of the council members, including China and Russia, abstained. Neighboring African countries have also discussed a coordinated armed intervention, but that has not garnered much support.
Conflict zone
Food insecurity
Forced migration
Heavy
Less
Famine
Emergency
Crisis
Stressed
Internally displaced camps
Refugee camps
White
Nile
SUDAN
ABYEI
Disputed
Malakal
KAFIA
KINDI
Bentiu
Disputed
UNITY
ETHIOPIA
Aweil
Nyirol
Mayendit Co.
Leer Co.
Akobo
Famine
An estimated 53,880 people have migrated to Sudan this year, many from Northern Bahr el Ghazal, because they have little access to food.
Famine
Wau
Uror
Akobo
Fighting in Uror County between government troops and armed opposition in mid-February displaced an estimated 13,000 to Akobo and Nyirol counties.
Rumbek
CENTRAL
AFRICAN
REP.
Bor
SOUTH SUDAN
Juba
Mountain
Nile
KENYA
CONGO
Attacks between 2014-2017 were used to map the conflict zones.
UGANDA
50 MILES
Both the rebels and the government have made it difficult for aid workers to reach the most-affected counties. The Washington Post’s Africa correspondent, Kevin Sieff, recently reported on the government’s obstructionism.
“Some of their actions appear to be brute thuggery, like the theft by soldiers last summer of more than 4,000 tons of food from a warehouse in Juba, the capital, enough to feed 220,000 people for a month,” he wrote. “But aid workers fear the government is intentionally denying aid to regions where it believes residents support the rebels.”
Sieff described how, at more than 70 checkpoints on the road between Juba and Unity State, soldiers would often demand bribes or food from aid workers, and how the government refuses to let the United Nations operate flights that could drop food aid over areas at risk of famine. Dozens of aid workers attempting workarounds have been killed in the war’s crossfire.
The United States and others in the U.N. Security Council have proposed an arms embargo to limit the South Sudan government’s capacity for violence. But when it came to a vote last December, more than half of the council members, including China and Russia, abstained. Neighboring African countries have also discussed a coordinated armed intervention, but that has not garnered much support.
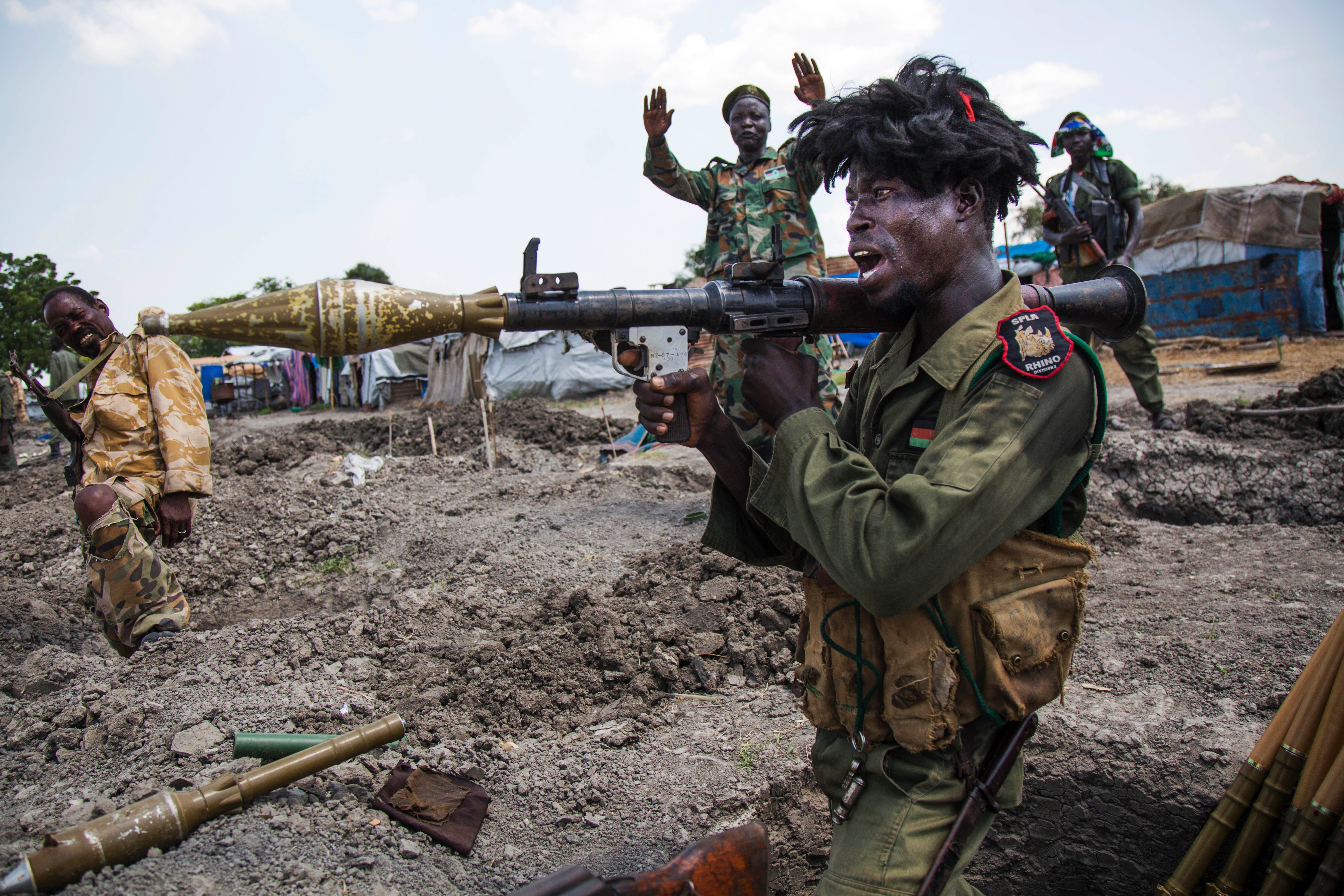 Soldiers of the Sudan People Liberation Army (SPLA) celebrate while standing in trenches in Lelo, outside Malakal on Oct. 16, 2016.
Soldiers of the Sudan People Liberation Army (SPLA) celebrate while standing in trenches in Lelo, outside Malakal on Oct. 16, 2016.
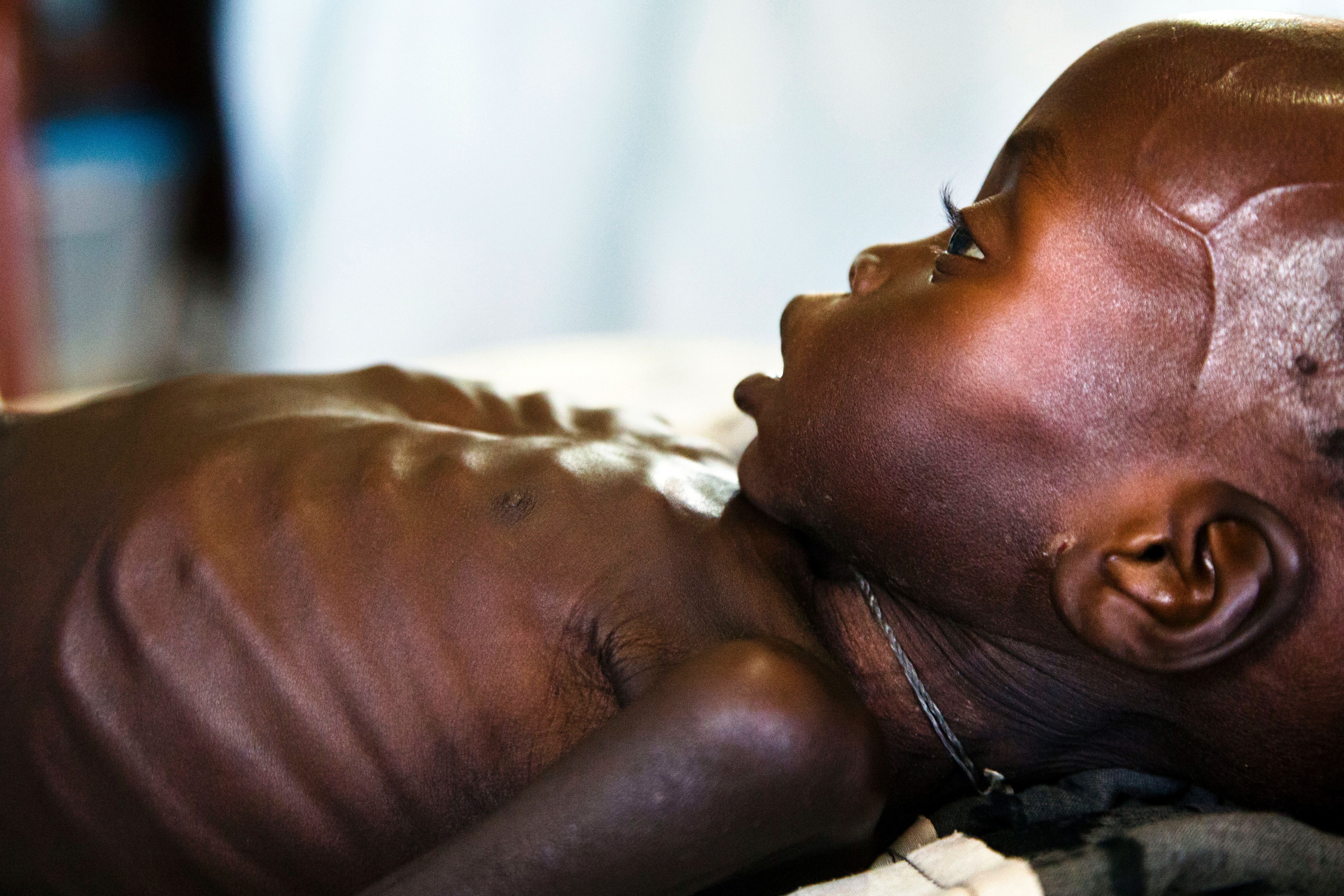 Agop Manut (11 months), who suffers acute malnutrition and respiratory distress, is assisted at the clinic run by Doctors without Borders (MSF) in Aweil. Images by Albert Gonzalez Farran/AFP/Getty Images
Civil war leaves Yemen splintered and under siege
A Yemeni woman inspects the damage at a factory allegedly targeted by Saudi-led airstrikes in Sanaa
Agop Manut (11 months), who suffers acute malnutrition and respiratory distress, is assisted at the clinic run by Doctors without Borders (MSF) in Aweil. Images by Albert Gonzalez Farran/AFP/Getty Images
Civil war leaves Yemen splintered and under siege
A Yemeni woman inspects the damage at a factory allegedly targeted by Saudi-led airstrikes in Sanaa
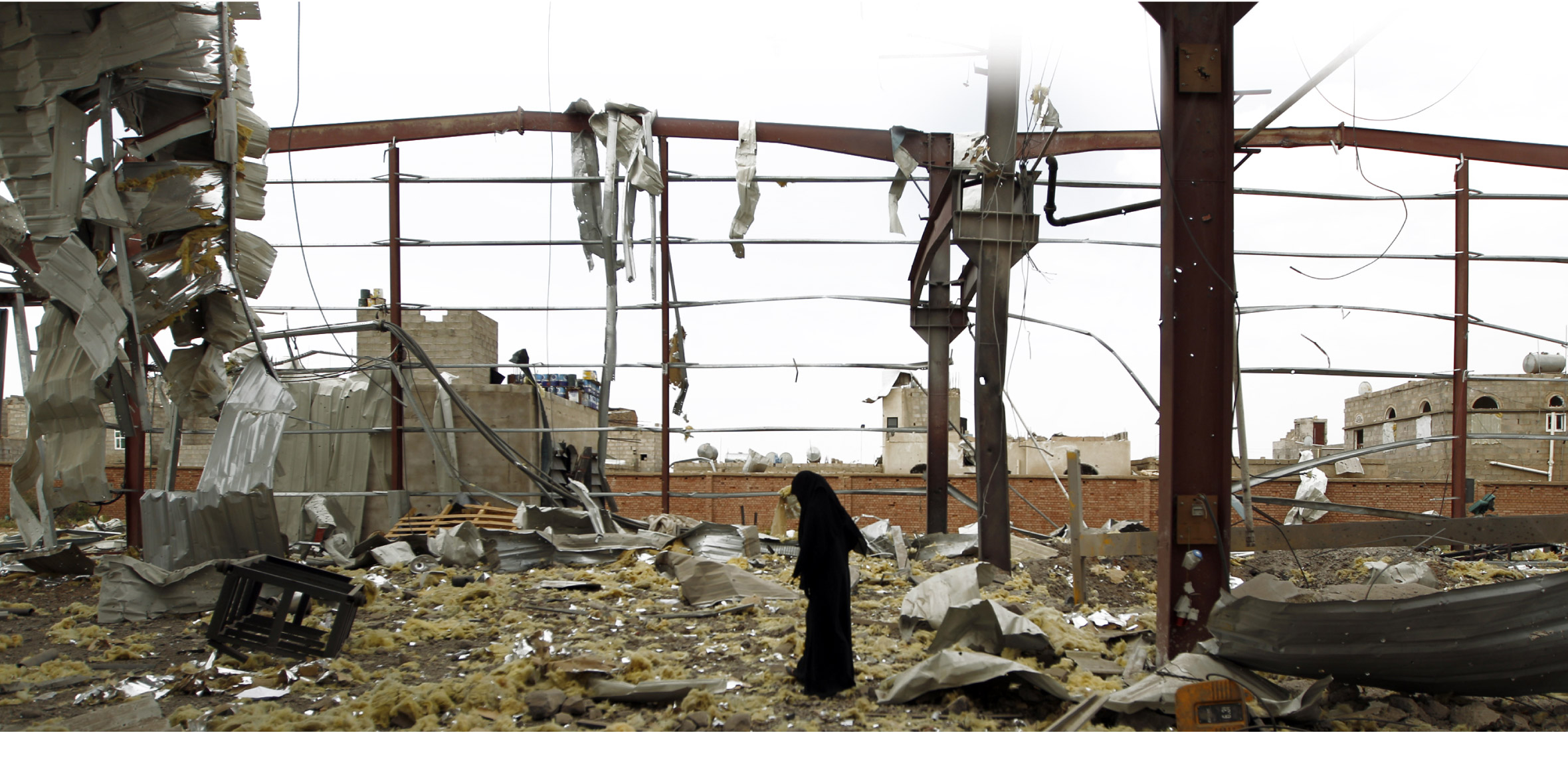 (Mohammed Huwais/AFP/Getty Images)
Since 2015, Yemen has been in a civil war. The fighting has divided control of the country along sectarian and ideological lines, and resulted in the deaths of more than 10,000. It has also decimated Yemen’s economy.
Yemen was fragile before the war, but its currency, industry, transport infrastructure and public services have all but been destroyed in the past two years. Millions are jobless, and food and fuel prices have shot through the roof. An estimated 17 million people, or 60 percent of the country’s population, are in need of urgent humanitarian assistance; about 7 million are living day-to-day, enduring until they wither away.
The physical destruction has mostly been the work of the Saudi Arabian-led coalition -- advised and supplied by the United States, Britain, and others -- that has sided with Yemen’s Sunni president against the Houthis, an armed Shiite militia that now controls the capital, Sanaa, and much of the country’s western coast.
(Mohammed Huwais/AFP/Getty Images)
Since 2015, Yemen has been in a civil war. The fighting has divided control of the country along sectarian and ideological lines, and resulted in the deaths of more than 10,000. It has also decimated Yemen’s economy.
Yemen was fragile before the war, but its currency, industry, transport infrastructure and public services have all but been destroyed in the past two years. Millions are jobless, and food and fuel prices have shot through the roof. An estimated 17 million people, or 60 percent of the country’s population, are in need of urgent humanitarian assistance; about 7 million are living day-to-day, enduring until they wither away.
The physical destruction has mostly been the work of the Saudi Arabian-led coalition -- advised and supplied by the United States, Britain, and others -- that has sided with Yemen’s Sunni president against the Houthis, an armed Shiite militia that now controls the capital, Sanaa, and much of the country’s western coast.
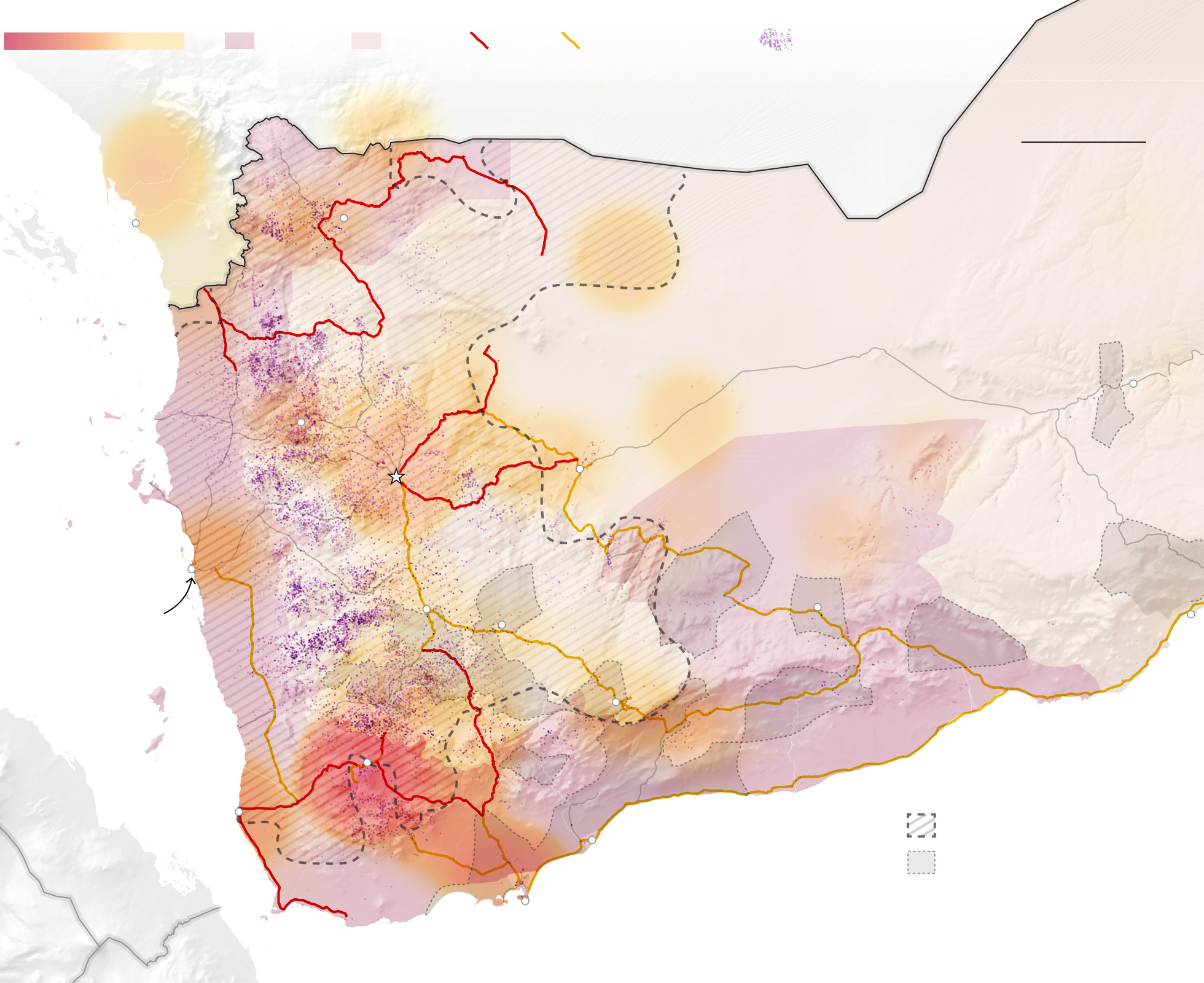 128%
Conflict zone
Food insecurity
Road conditions
Forced migration
Heavy
Less
Emergency
Crisis
Closed
Difficult to access
Internally displaced site
SAUDI ARABIA
50 MILES
Sadah
Jizan
YEMEN
Seiyun
Red
Sea
Hajjah
Sanaa
Marib
Hodeida
Dhamar
Ataq
Al Mukalla
Rada’a
Saudi ships are currently enforcing a near total blockade of this port.
Al Bayda
Taizz
Territorial control
Mocha
Houthi controlled area
Zinjibar
ERITREA
District where al-Qaeda in the
Arabian Peninsula has claimed
an attack since Nov. 2016.
Gulf of Aden
Aden
Bab el-Mandeb
Strait
DJIB.
Attacks between 2014-2017 were used to map the conflict zones.
128%
Conflict zone
Food insecurity
Road conditions
Forced migration
Heavy
Less
Emergency
Crisis
Closed
Difficult to access
Internally displaced site
SAUDI ARABIA
50 MILES
Sadah
Jizan
YEMEN
Seiyun
Red
Sea
Hajjah
Sanaa
Marib
Hodeida
Dhamar
Ataq
Al Mukalla
Rada’a
Saudi ships are currently enforcing a near total blockade of this port.
Al Bayda
Taizz
Territorial control
Mocha
Houthi controlled area
Zinjibar
ERITREA
District where al-Qaeda in the
Arabian Peninsula has claimed
an attack since Nov. 2016.
Gulf of Aden
Aden
Bab el-Mandeb
Strait
DJIB.
Attacks between 2014-2017 were used to map the conflict zones.
One key piece of infrastructure that the coalition has made near-inoperable is the Houthi-controlled port of Hodeida, Yemen’s largest and most vital. Almost 90 percent of Yemen’s food is imported, and most of it came through Hodeida. Saudi ships are currently enforcing a near total blockade of the port, arguing that they can’t risk arms smuggling even though the United Nations inspects each ship on arrival.
Should the coalition move to take Hodeida’s city and port militarily, it could shut off what trickle of food is left to Sanaa and other highly populated inland areas, triggering a famine, according to aid agencies. Coalition officials, on the other hand, have argued that if they took the port, they could ensure the passage of aid without worrying about arms smuggling.
Either way, vast swaths of Yemen are under constant bombardment from the coalition, which has reduced markets, factories, hospitals, roads and bridges to rubble. Three quarters of the residents of the city of Taizz and its surrounding areas, for instance, are facing an emergency food shortage because the area is effectively inaccessible. Saudi Arabia maintains that it does all it can to avoid civilian casualties, but human rights groups have documented countless strikes on seemingly nonstrategic targets.
Yemen’s food crisis is expected to deteriorate as international traders become less and less likely to do business in a country without a functioning central bank and currency. The fate of millions also hangs on what happens in Hodeida, which is likely to be the scene of a major battle in the near future.
WP-Famine-08-YemenL.jpg'>
aida Ahmad Baghili, an 18-year-old Yemeni, sits in a wheelchair at the Al-Thawra Hospital in Hodeidah, where she is receiving treatment for severe malnutrition. (AFP/Getty Images)
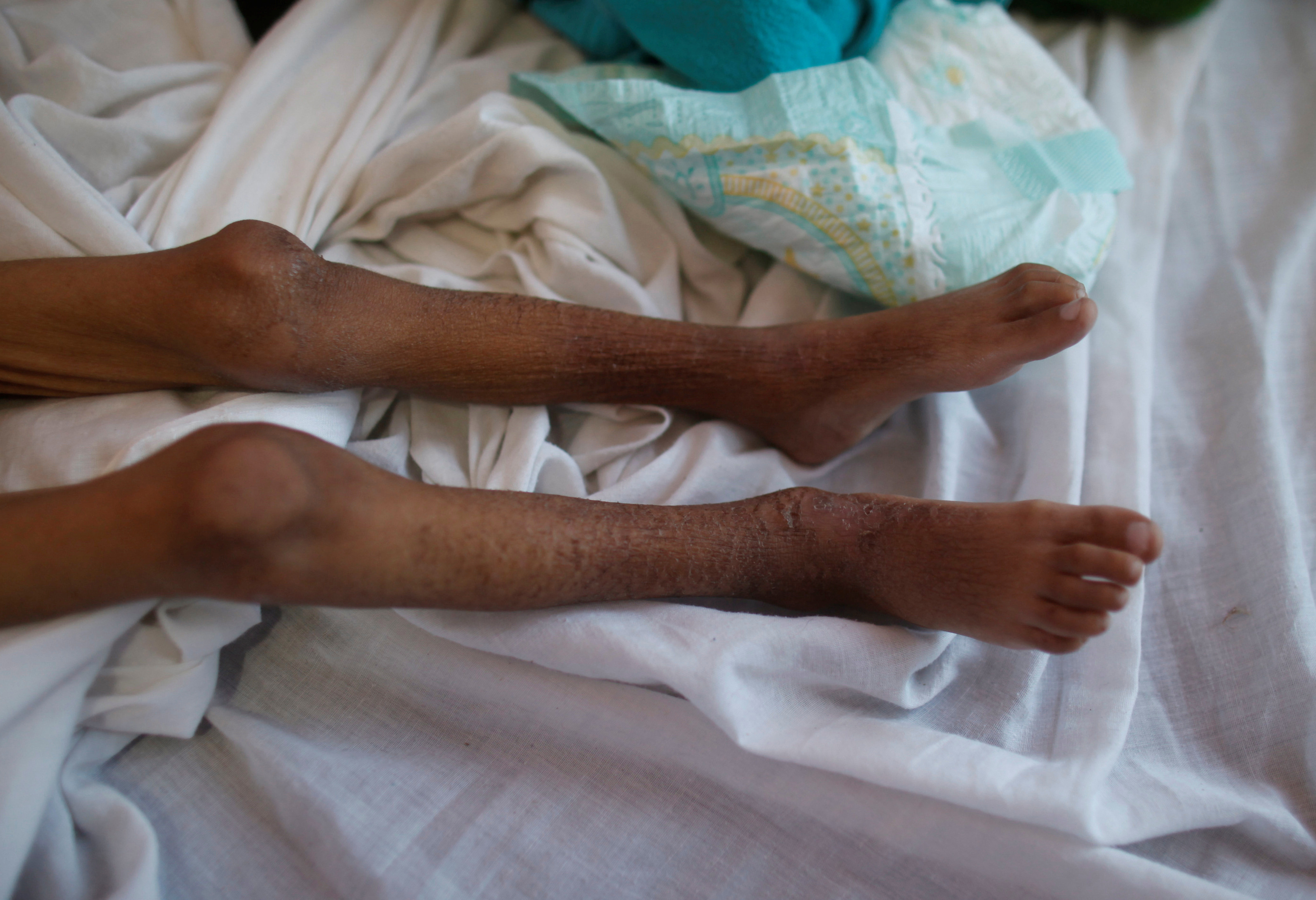 The legs of a malnourished boy who was being treated last year at a medical center in Sanaa, Yemen. (Khaled Abdullah/Reuters)
The legs of a malnourished boy who was being treated last year at a medical center in Sanaa, Yemen. (Khaled Abdullah/Reuters)
Eight years of terror create a nightmare in northeastern Nigeria
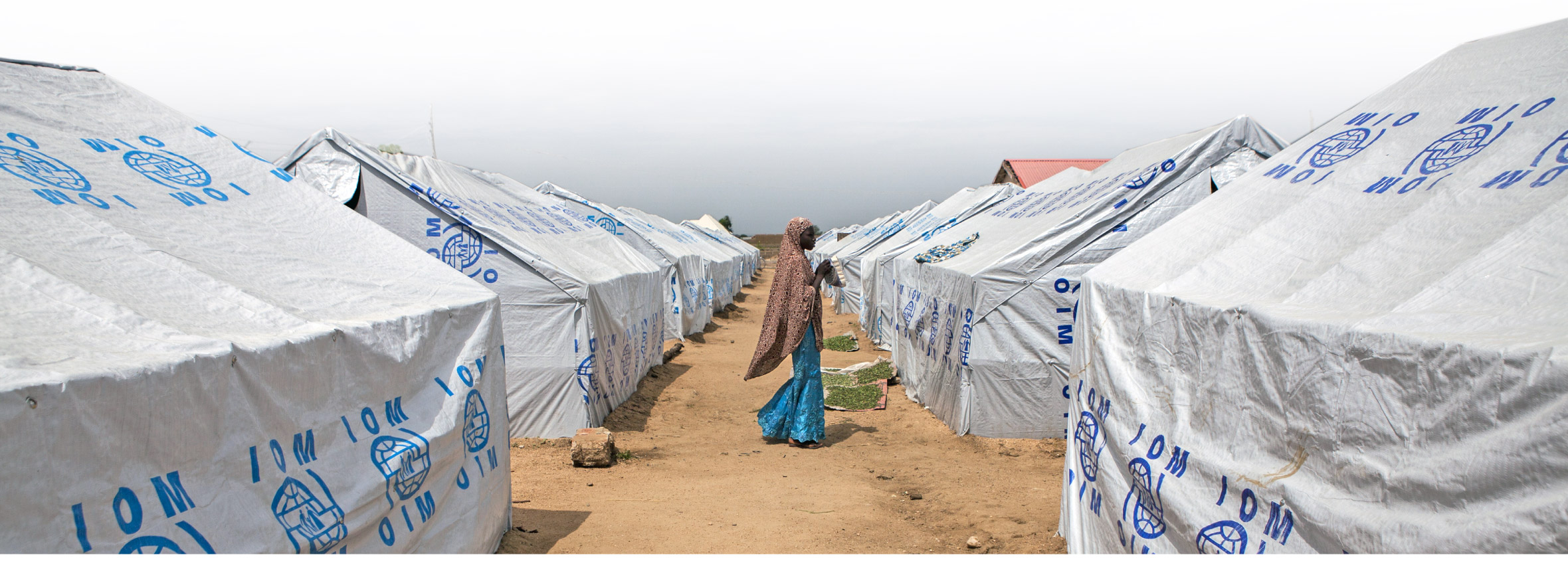
A woman walks between tents erected by the International Organization for Migration in Gwoza.
(Jane Hahn for The Washington Post)
Boko Haram’s bloody reign of terror in northeastern Nigeria’s Borno State has been so intense over the past few years that aid groups have struggled to even enter the region. Reliable data on hunger is limited. Some aid workers speculate that Borno may have already passed through periods of famine, or may be in one now.
The fighting has displaced more than 3 million people, and left a previously fertile region desiccated and barren. Vast camps have sprung up within Nigeria, as well as across the borders in Niger and Cameroon. The population of the relatively safe capital of Borno, Maiduguri, has doubled because of the influx, and the city is now a hub for disease. Tens of thousands of Nigerians, meanwhile, have set their sights north, across the Sahara, toward Libya and ultimately Europe, attempting an expensive and dangerous trip that many do not survive.

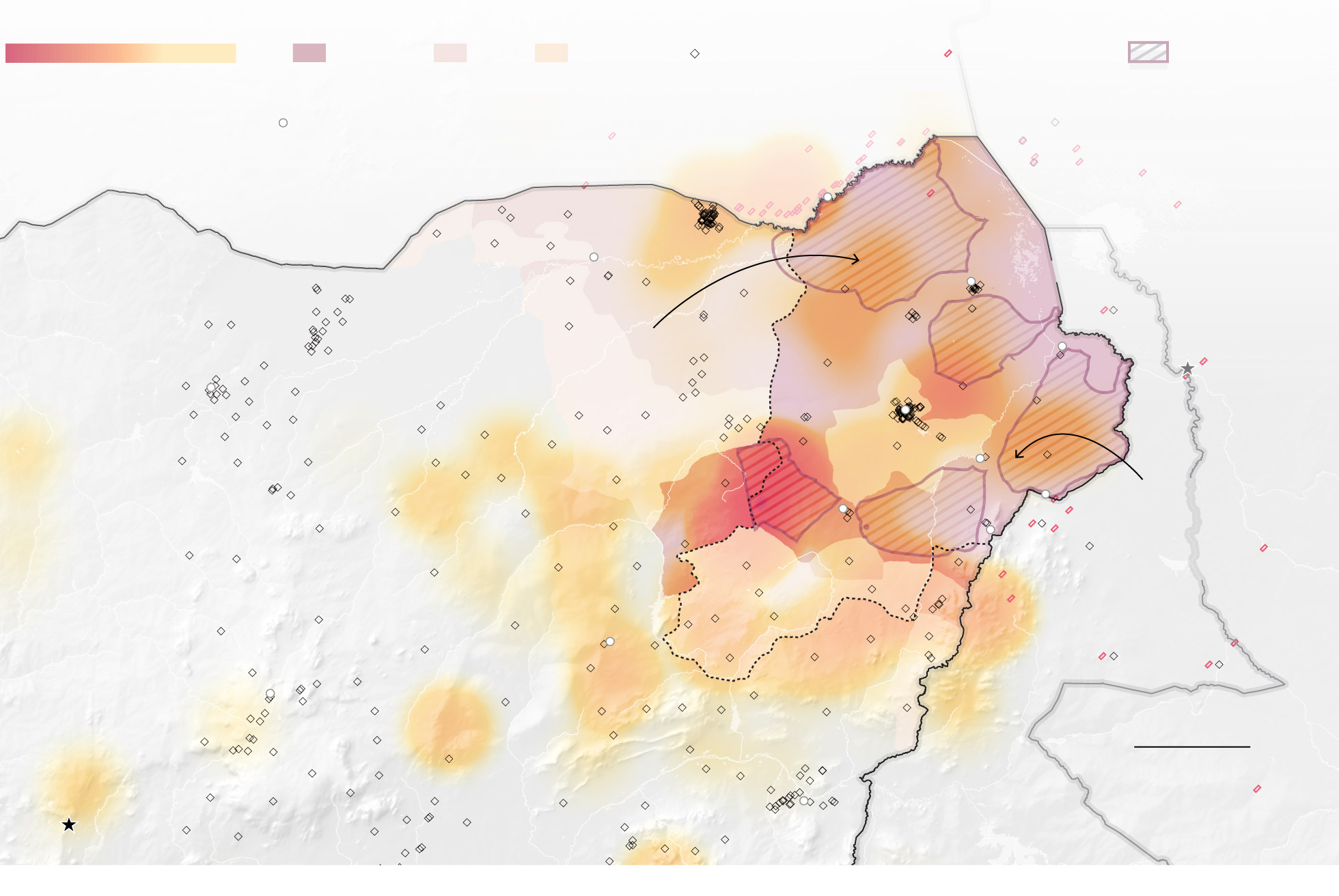 Conflict zone
Food insecurity
Forced migration
Humanitarian aid
Heavy
Less
Emergency
Crisis
Stressed
Internally displaced camps
Refugee camps
Area inaccessible
Zinder
CHAD
NIGER
Diffa
Lake Chad
Gashua
Monguno
BORNO
The risk of famine in inaccessible areas of Borno State will remain high over the coming year.
Ngala
Kano
Ndjamena
Maiduguri
Bama
Banki
A famine likely occurred in Bama and Banki towns during 2016 but could not be verified.
Damboa
Gwoza
NIGERIA
Gombe
CAMEROON
Jos
50 MILES
Abuja
Yola
Conflict zone
Food insecurity
Forced migration
Humanitarian aid
Heavy
Less
Emergency
Crisis
Stressed
Internally displaced camps
Refugee camps
Area inaccessible
Zinder
CHAD
NIGER
Diffa
Lake Chad
Gashua
Monguno
BORNO
The risk of famine in inaccessible areas of Borno State will remain high over the coming year.
Ngala
Kano
Ndjamena
Maiduguri
Bama
Banki
A famine likely occurred in Bama and Banki towns during 2016 but could not be verified.
Damboa
Gwoza
NIGERIA
Gombe
CAMEROON
Jos
50 MILES
Abuja
Yola
Attacks attributed to Boko Haram between 2014-2017 were used to map the conflict zones.
Almost as many as those who have fled Boko Haram-controlled areas have stayed behind. Those people are most at risk of starvation, because their villages are inaccessible to outside aid.
Nigeria’s military, even in cooperation with neighboring countries and U.S. and British advisers, has proved sorely inadequate in rooting out the insurgency, although they have made some progress. When they have succeed in liberating towns and villages from Boko Haram, they often find residents eating grass and insects because that’s all that’s left.
The United Nations. has warned that half a million children in northeastern Nigeria are so severely malnourished that 75,000 could die by June. A growing measles outbreak in the region could transform into an epidemic, too.
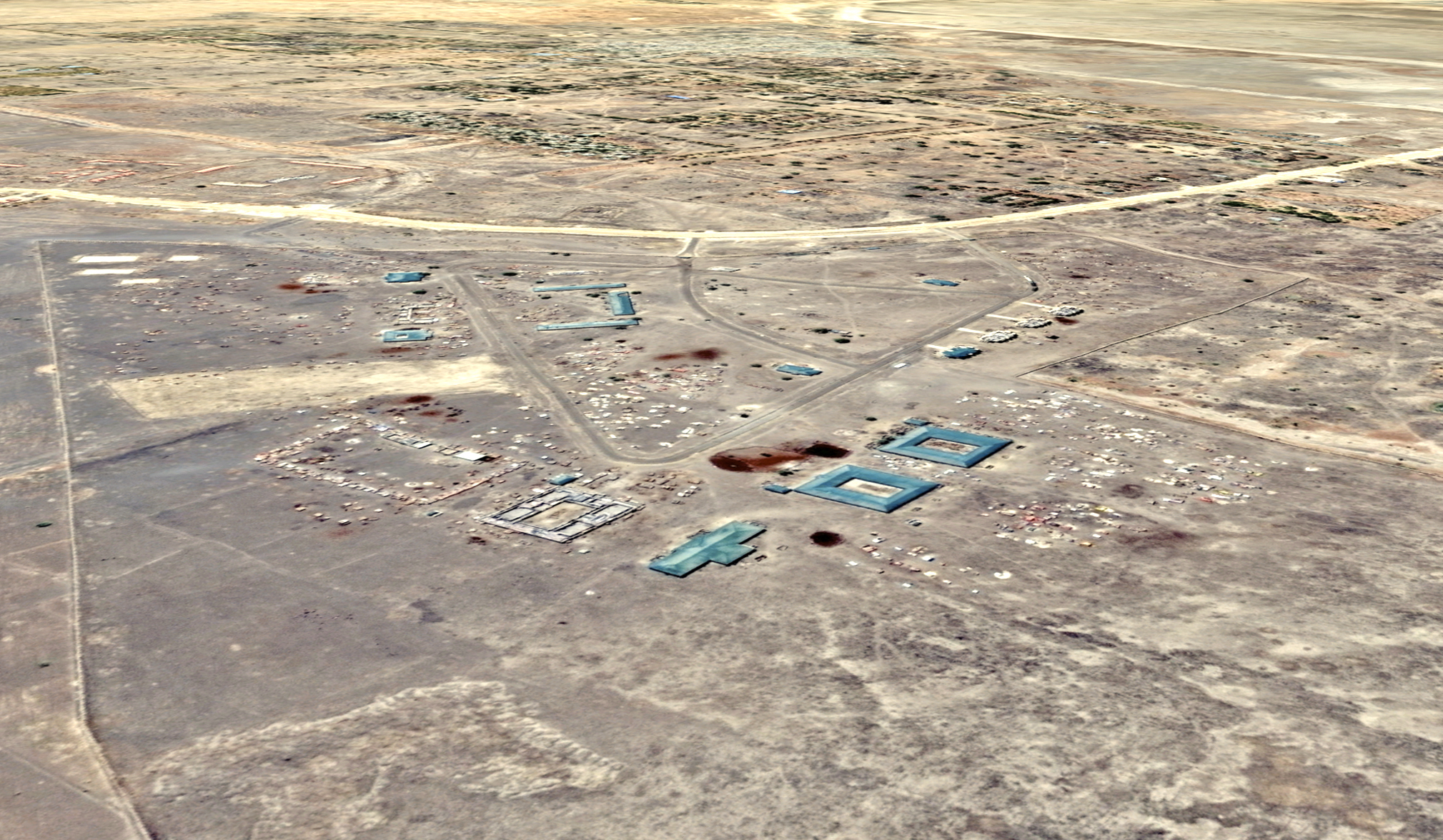
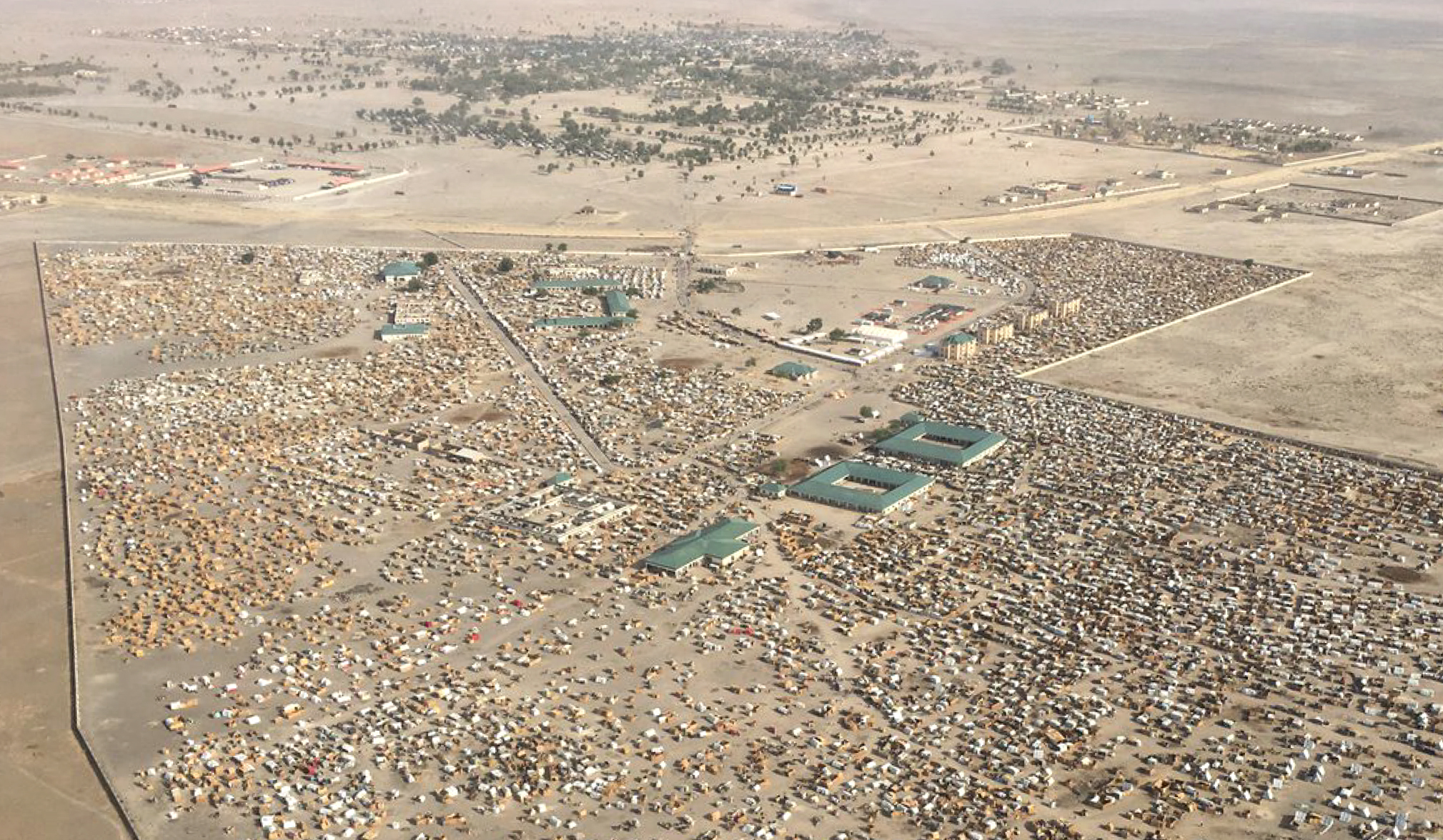
 SLIDE
Ngala 2017
Ngala 2016
SLIDE
Ngala 2017
Ngala 2016
The Nigerian border town of Ngala has seen a camp grow to 74,000 displaced people in a year. (2017 image via U.N. and 2016 image GoogleEarth via DigitalGlobe)
Because of the struggle to gain access to the most critically affected people, organizations realized the scale of the crisis in Nigeria long after malnutrition was rife. Much of the blame falls on the Nigerian government’s lack of response, according to aid workers. Despite having the continent’s largest economy, the country’s leaders have failed to address the hunger emergency in Borno.
 Women wait for food to be distributed at the Government Girls Secondary School IDP camp in Monguno, Nigeria.
Women wait for food to be distributed at the Government Girls Secondary School IDP camp in Monguno, Nigeria.
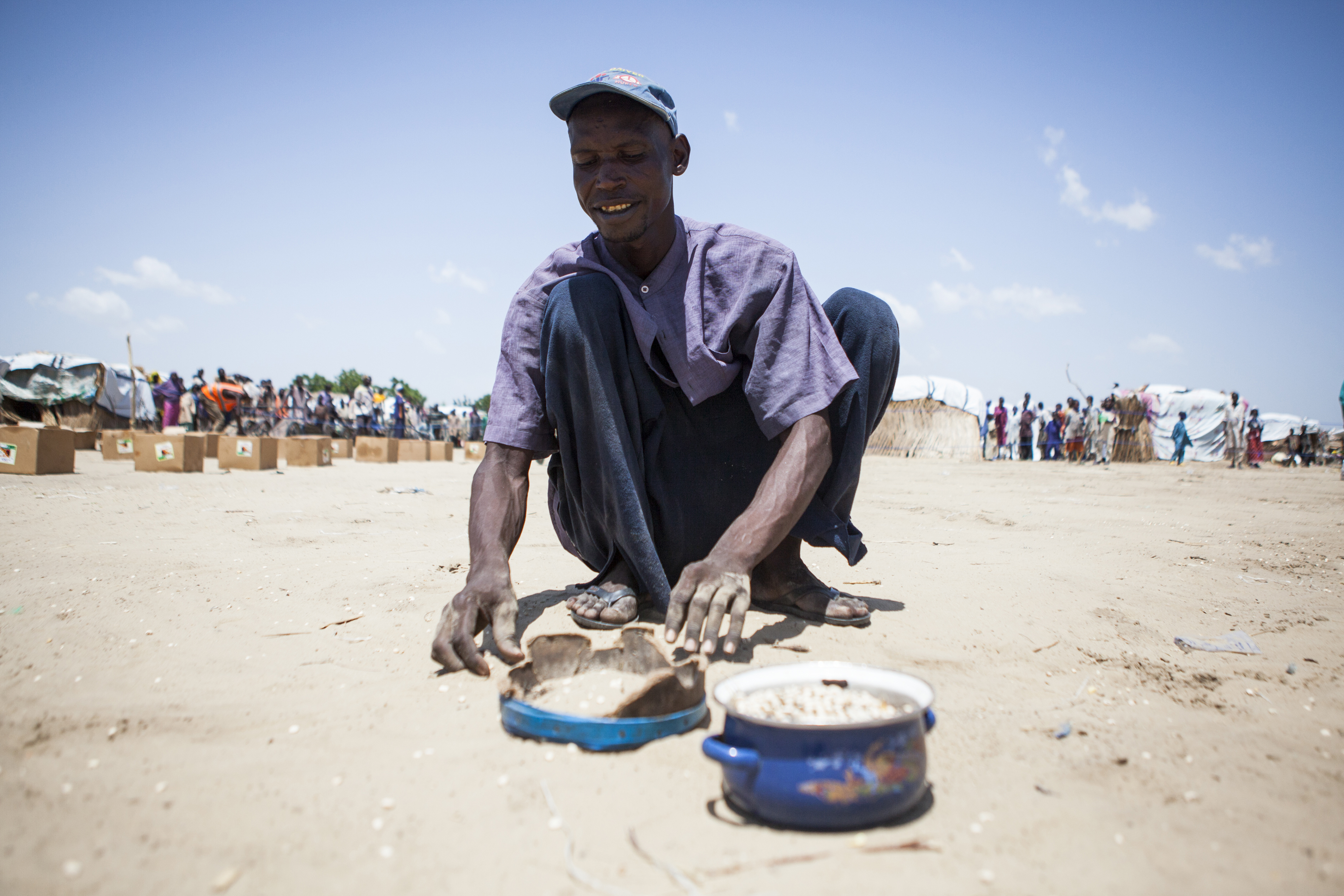 Hamadu Husseiny, 28, searches for beans that have fallen during a food distribution in Monguno. (Photos by Jane Hahn for The Washington Post)
Hamadu Husseiny, 28, searches for beans that have fallen during a food distribution in Monguno. (Photos by Jane Hahn for The Washington Post)
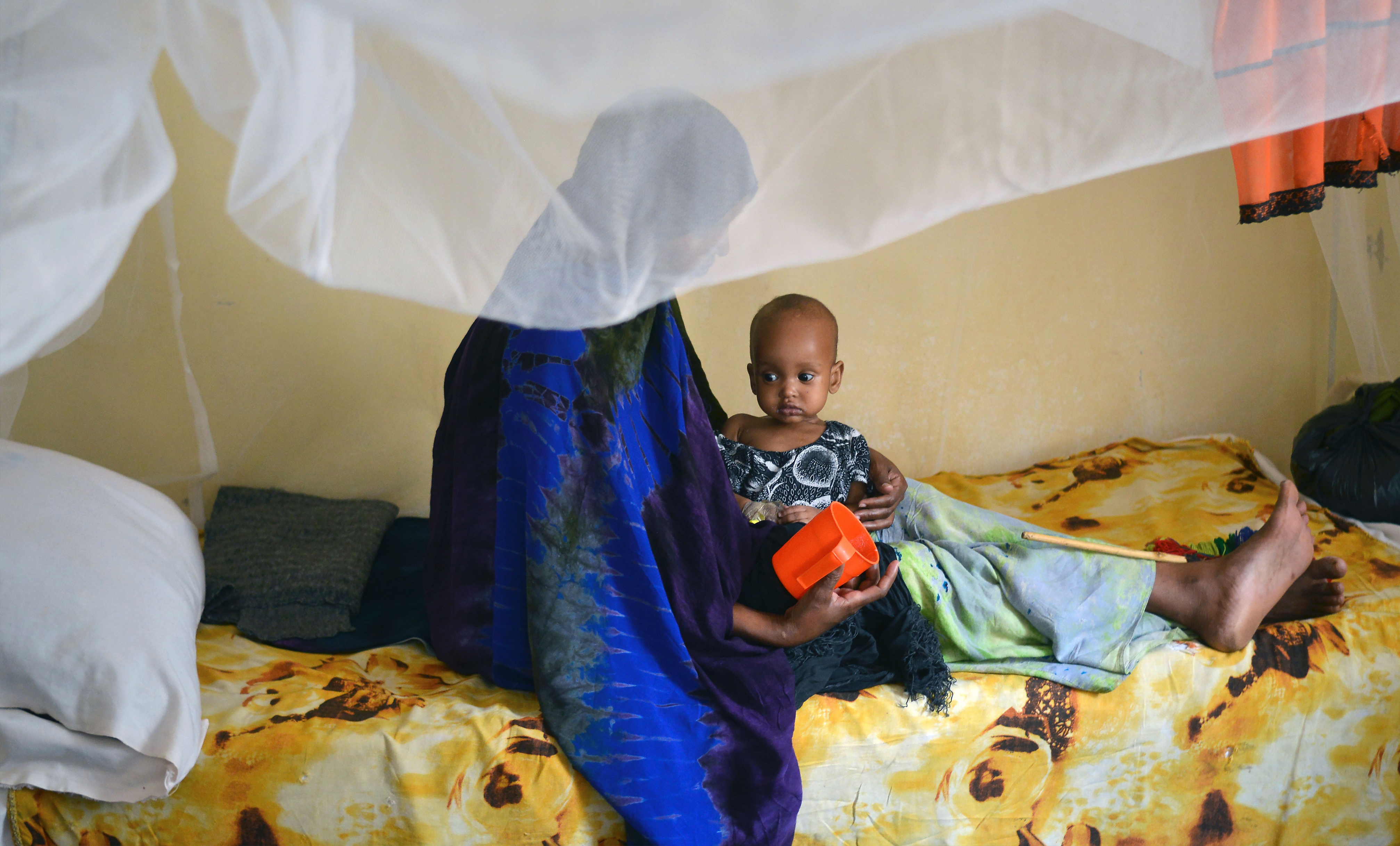
A drought in Somalia, a land awash with guns
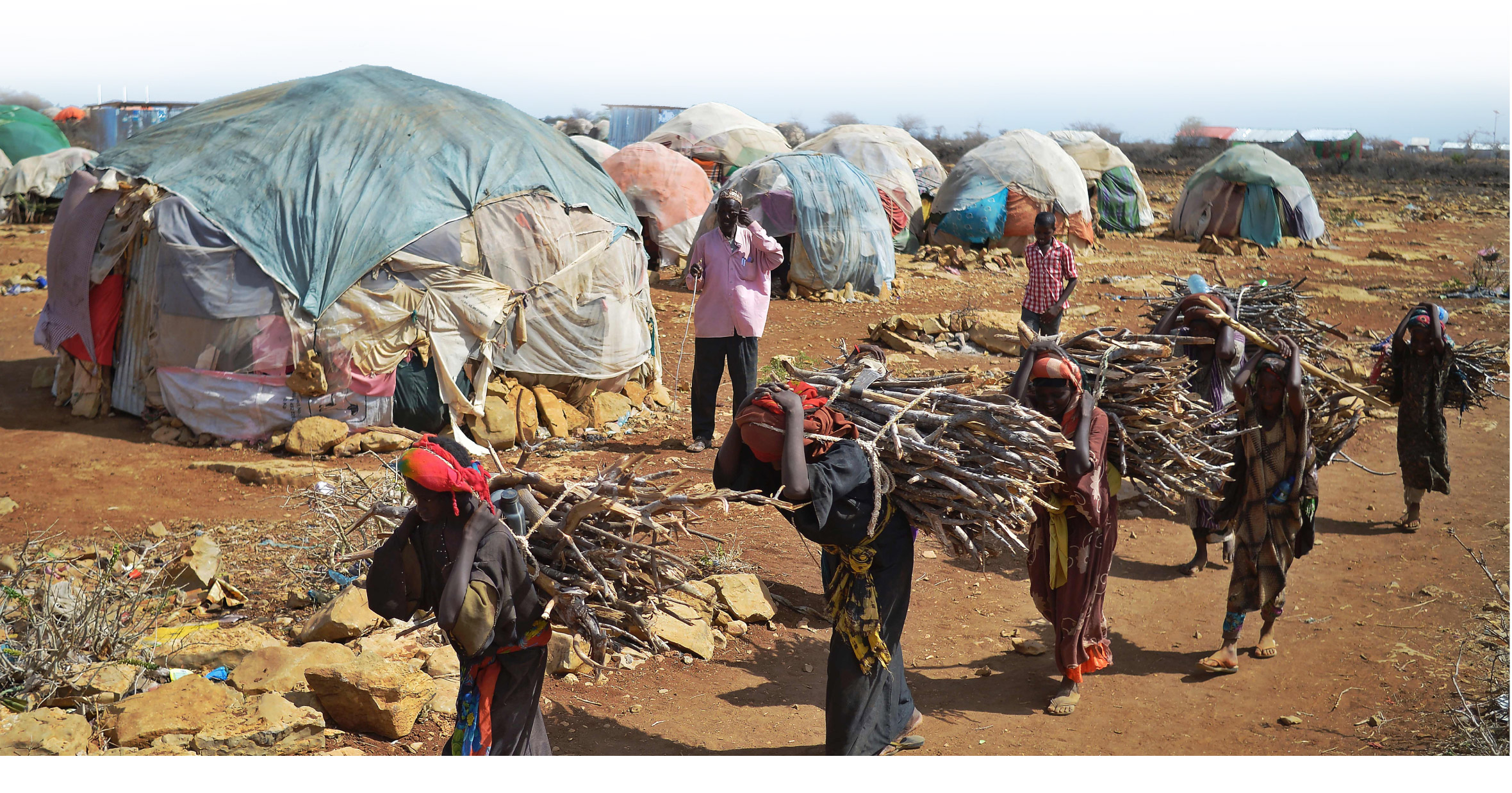 Women carry firewood as they walk back to a makeshift camp on the outskirts of Baidoa where thousands of internally displaced people arrive daily after they fleeing the parched countryside.
Women carry firewood as they walk back to a makeshift camp on the outskirts of Baidoa where thousands of internally displaced people arrive daily after they fleeing the parched countryside.
(Tony Karumba/AFP/Getty Images)
Six years ago, more than a quarter of a million Somalis died in a famine. The rains have now failed for two consecutive years in parts of the country, and there are growing fears of a repeat catastrophe. But droughts are common in Somalia, and do not always result in famine. The common link between 2011 and today is the continued presence of al-Shabab, an armed group closely linked with al-Qaeda.
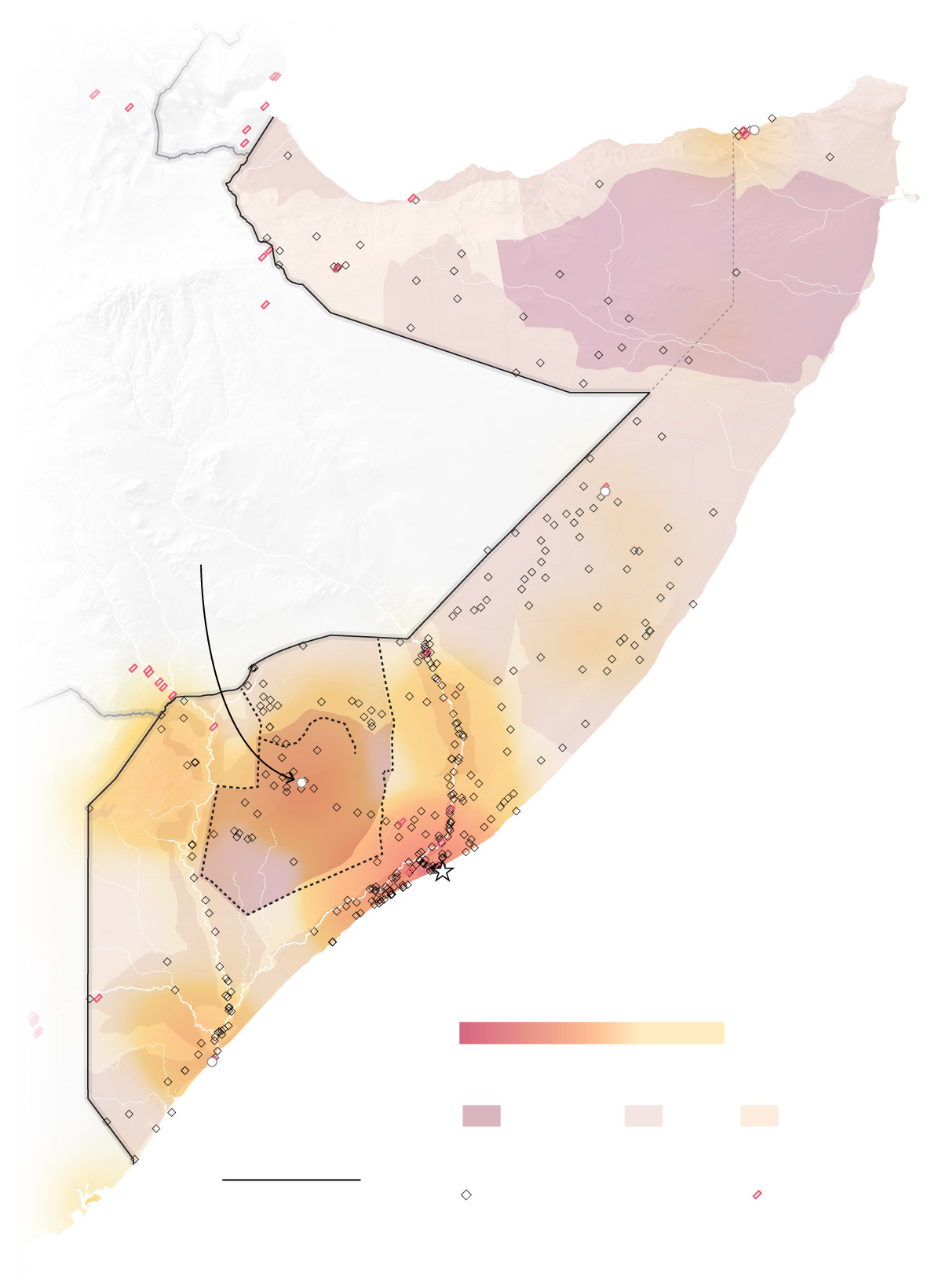 Gulf of Aden
DJIB.
Bosaso
SOMALILAND
Disputed
ETHIOPIA
PUNTLAND
Gaalkacyo
Some 81,000 people have arrived in Baidoa since November.
SOMALIA
BAKOOL
Baidoa
Indian Ocean
BAY
Mogadishu
Conflict zone
Heavy
Less
Kismaayo
Food insecurity
Emergency
Crisis
Stressed
Forced migration
KENYA
Internally displaced camps
Refugee camps
100 MILES
Gulf of Aden
DJIB.
Bosaso
SOMALILAND
Disputed
ETHIOPIA
PUNTLAND
Gaalkacyo
Some 81,000 people have arrived in Baidoa since November.
SOMALIA
BAKOOL
Baidoa
Indian Ocean
BAY
Mogadishu
Conflict zone
Heavy
Less
Kismaayo
Food insecurity
Emergency
Crisis
Stressed
Forced migration
KENYA
Internally displaced camps
Refugee camps
100 MILES
Attacks attributed to al-Shabaab between 2014 - 2017 were used to map the conflict zones.
While al-Shabab has lost ground since 2011, the famine risk in Somalia is concentrated in rural areas in the country’s south, where the group is still strong. That is because the militant group severely restricts the movement of locals who may be in search of scarce food and water. They also restrict access to aid.
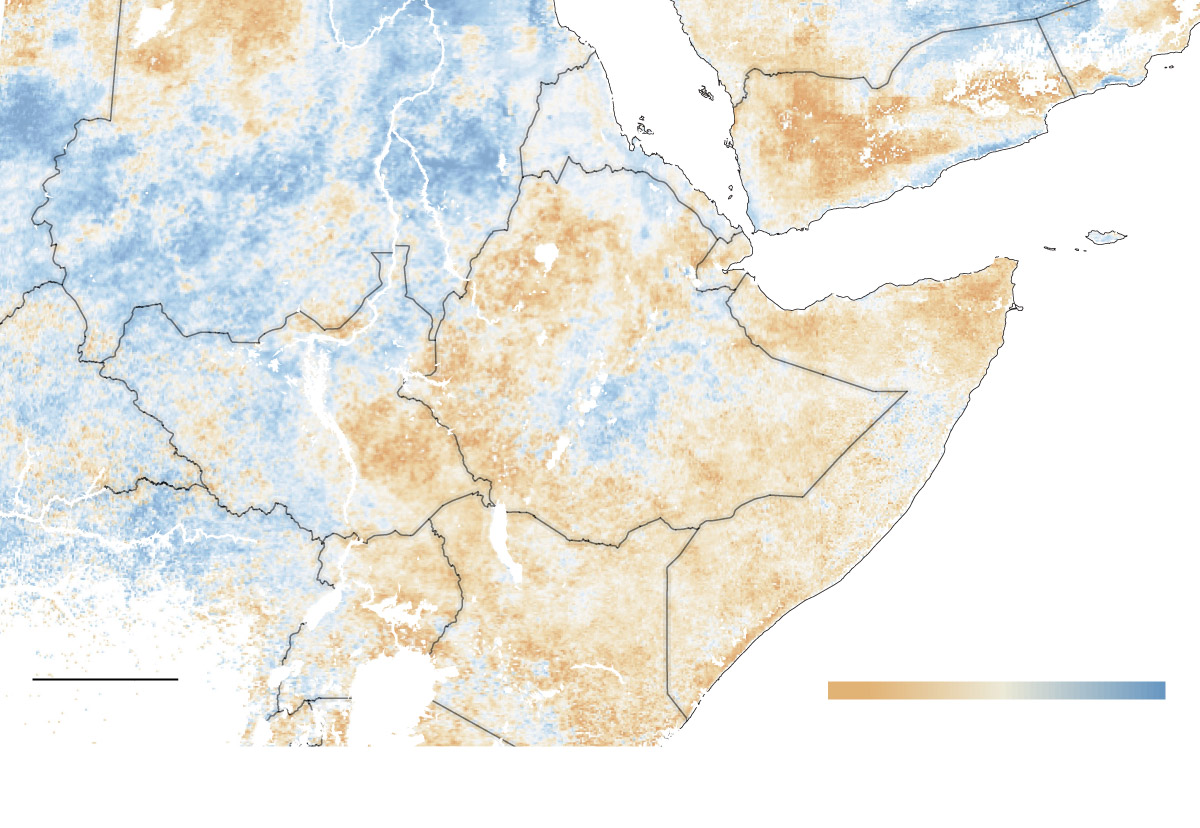 YEMEN
SUDAN
ETHIOPIA
S. SUDAN
SOMALIA
KENYA
Drought conditions
Nov. 2016 - Feb. 15 2017
300 MILES
More
Less
YEMEN
SUDAN
ETHIOPIA
S. SUDAN
SOMALIA
KENYA
Drought conditions
Nov. 2016 - Feb. 15 2017
300 MILES
More
Less
Evaporative stress map by Joshua Stevens and Christopher Hain/NASA MSFC using USDA Hydrology and Remote Sensing Lab data.
Yet Somalia, surprisingly, is where there is the most optimism at averting a famine. Despite the fighting, al-Shabab has recently given assurances that it will allow for freer movement of people. The power of the group has also declined significantly, meaning that climatic conditions contribute more to Somalia’s crisis proportionally than the others.
And while a drought can leave a nation reliant on aid, that is ultimately an easier problem to solve than war.
 A malnourished child is fed a special formula by her mother at a regional hospital in Baidoa town. (Tony Karumba/AFP/Getty Images)
A malnourished child is fed a special formula by her mother at a regional hospital in Baidoa town. (Tony Karumba/AFP/Getty Images)
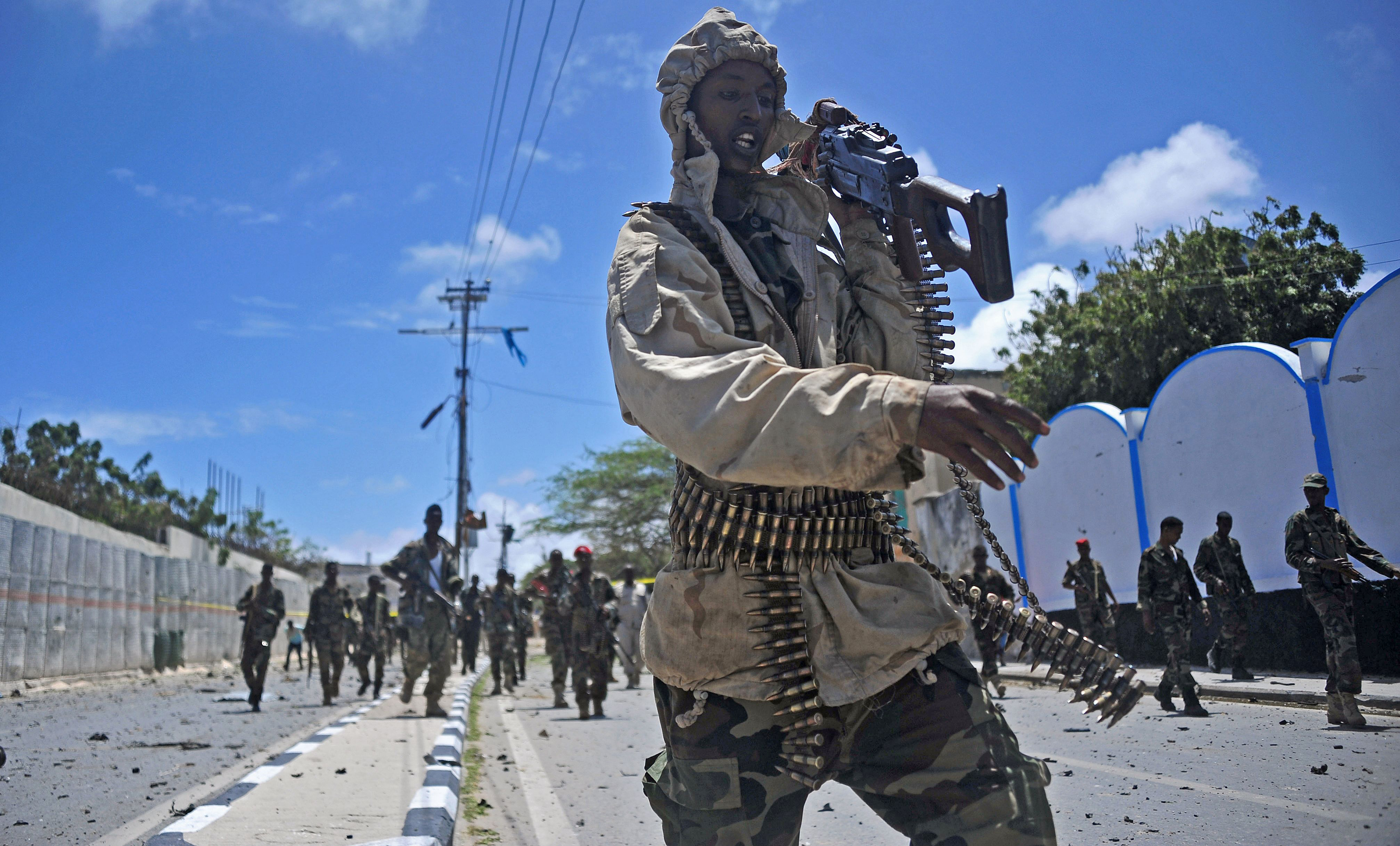 Somali security forces patrol the scene of a suicide car bomb blast on Aug. 30, 2016. in Mogadishu. Al-Shabab jihadists aligned with al-Qaeda claimed responsibility for the blast.(Mohamed Abdiwahab/AFP/Getty Images)
Somali security forces patrol the scene of a suicide car bomb blast on Aug. 30, 2016. in Mogadishu. Al-Shabab jihadists aligned with al-Qaeda claimed responsibility for the blast.(Mohamed Abdiwahab/AFP/Getty Images)
At this time of unprecedented need, the world’s biggest supplier of humanitarian relief is getting ready for a major cutback. Humanitarian aid makes up a tiny fraction of the U.S. government spending — less than 1 percent — but the Trump administration’s proposed budget would eliminate much of it. Although the cuts would have to withstand bipartisan opposition, the State Department and the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) could see their budgets reduced by more than a third. U.S. funding to the United Nations might drop by more than half.
The United Nations had sought $4.4 billion by the end of March for emergency hunger relief operations, but raised barely a fraction of that. Emergency funding doesn’t address the root causes of famine, nor can it always reach the worst-affected. But it can prevent the spread of disease and provide enough sustenance to the millions it does reach so that they might survive.
Sources: Conflict data via IHS Jane’s Terrorism & Insurgency Center. Food insecurity data via fews.net. Displaced persons camp data via UNHCR and immap.org via mal-khameri@immap.org. Yemen territorial control via criticalthreats.org. Drought data via NASA Earth Observatory.
----------------------------------------------
More stories
South Sudan’s people are starving, and fighters are blocking aid
A U.N. declaration of famine in February should have brought a surge of assistance, but within days, the South Sudanese government ordered aid workers to leave ahead of a planned offensive, and the area was soon consumed with fighting.
‘A famine unlike any we have ever seen’
As Nigeria battles Islamist terrorists, millions are at risk of starvation, and the world is barely aware.
The brutal toll of Boko Haram’s attacks on civilians
As the Islamic State’s attacks in Europe have captured the world’s attention, an ISIS-affiliated group has been waging an even deadlier campaign in Africa.