OVERVIEW
MANAGEMENT
PERFORMANCE
POSSIBILITIES
CAPITALS
ACTIVITIES
ACTORS
BURGESS
|
EXTREME WEATHER
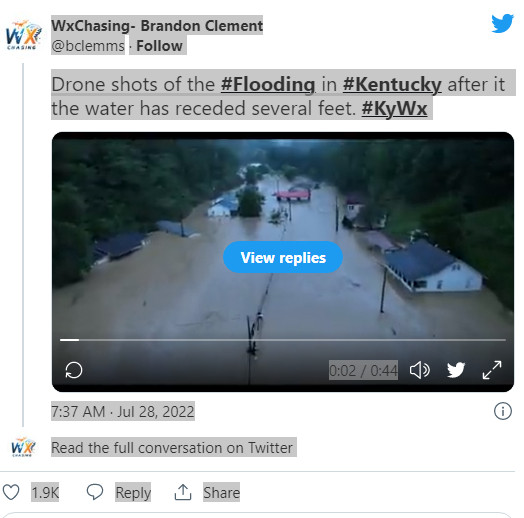
FLOODS Massive flooding in Kentucky engulfs homes, leaves at least 15 dead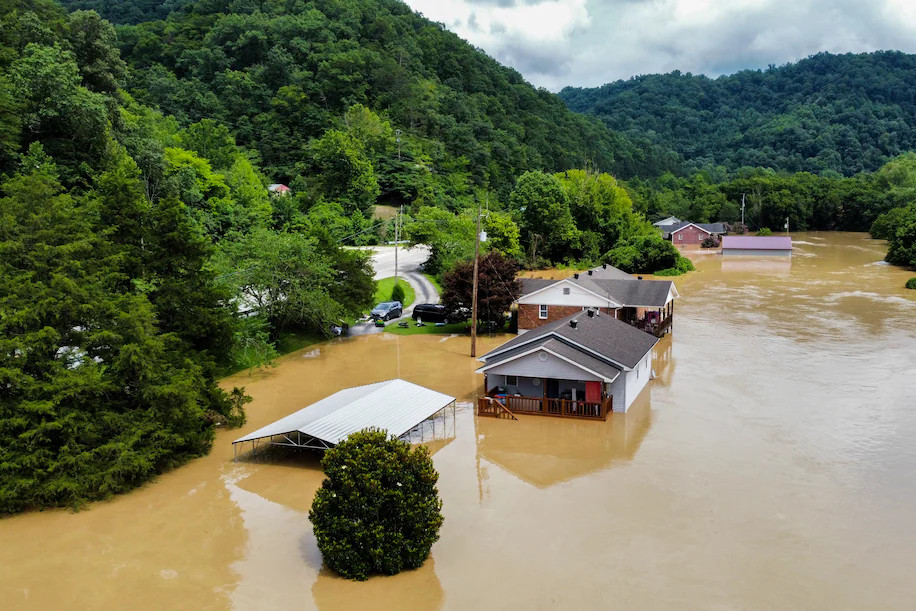 
Muddy water from a nearby river seeps into homes in Jackson, Ky., on July 28. (Arden S. Barnes for The Washington Post) Original article: https://www.washingtonpost.com/climate-environment/2022/07/28/kentucky-flooding-jackson-hazard/ Peter Burgess COMMENTARY For anyone with half a brain and a little curiosity, it has been obvious for many years ... like since the 1980s ... that there was climate change and most likely it was associated in some way with atmospheric pollution. I guess I have an advantage. In the late 1960s I was employed by a company called Aerosol Techniques Inc. (ATI) which dominated the production of aerosol products in the USA. When it was determined that Chlorofluorocarbons or CFCs were the main cause of ozone layer depletion in the atmosphere, our company moved rapidly to remove these items from our products. Sadly, they are still quite widely used in solvents, refrigerators, air-conditioners, etc. The management team at ATI prepared to accept scientific findings and act accordingly. ATI is no more, but this has nothing to do with thise decision, but other strategic decisions that did not work out well !!!!!! Another advantage I have is that my career has taken me to many different parts of the world. In many places people are closer to nature than in the ultra-comfortable air-conditioned USA. It has been apparent for a very long time that crops are not growing in the same way now than they did years ago. I worked in the Sahel in Africa in the 1980s after the record droughts in the 1970s. The climate has gone back to that period again in the last few years and population density is higher now than it was then. A slow moving diasster is in progress, but there is less international interest and involvement now than fifty years ago and a catastrophe will ensue. Already, there are many migrants from Africa trying to cross the Mediterranean into Europe because of poor conditions and prospects in Africa ... and it gets more serious year after year. Little has been done by the international community to address this problem. The committment to any sort of assistance seems to be much less now than it was several decades ago. There are geopolitical reasons for this that should be better understood ... but that is for another time. The floods in Kentucky being described here are worse than anything yet ... something of a confirmation of what scientists have been saying for years, that there will be growing instability in the behavior of the weather with more rain and more drought, more cold and more heat and more violent storms more often. That is what we are now seeing ... and it comes as no surprise to those who have been paying even a small amount of attention to the met data. I don't hear much conversation about what should be done to compensate people for the costs of these disasters. There are some very big numbers referenced in news programs when the disaster is in progress, but much less over the weeks and months and years it takes to recover ... or not. I know that the insurance industry has started to pay more attention to the costs they will have to address in the future ... but my impression is that it is modest compared to what is likely. It is more than a decade ago that I tried to point out that most insurance companies would go out of business if they faced up to their future liabilities in an honest way ... but, needless to say, this was not a popular point of view in the insurance industry !!!!!!!! And now there is the record breaking flooding in Kentucky !!!!!!! Peter Burgess | ||
|
Massive flooding in Kentucky engulfs homes, leaves at least 15 dead
The death toll could rise significantly after a deluge submerged homes, swept cars away, and heavily damaged roads and other infrastructure Written by the CAPITAL WEATHER GANG ... Rick Childress, Ian Livingston, Lateshia Beachum and Jason Samenow ... Annie Gowen, Teddy Amenabar and Andrea Sachs contributed to this report. Published July 28, 2022 at 11:55 a.m. EDT ... Updated July 29, 2022 at 8:23 a.m. EDT JACKSON, Ky. — A new round of catastrophic flooding struck the central United States on Thursday, swamping communities in the Appalachian foothills of eastern Kentucky, leaving more than a dozen people dead and several others missing or trapped. On Friday morning, Gov. Andy Beshear (D) said that at least 15 people — including children — had died in the flooding, according to the Associated Press. Beshear called the event “one of the worst, most devastating flooding events in Kentucky’s history,” saying officials expect “double-digit deaths” and describing how rescuers were finding people stranded on rooftops. “I do believe it will end up being one of the most significant deadly floods that we have had in Kentucky in at least a very long time,” he said. Beshear confirmed the death of an 81-year-old woman in Perry County, along with two other deaths in Perry and Knott counties. Later Thursday, he confirmed five additional fatalities and warned that, with more rain on the way, the danger was not over. He said 20 to 30 people had been airlifted to safety. “This isn’t just a disaster; it’s an ongoing natural disaster,” Beshear said. “We are in the midst of it, and for some places, it will continue through tonight.” Images shared on social media show houses submerged to their roofs, cars swept away, and serious damage to roadways and other infrastructure. Local television crews broadcast videos of rescuers in boats and helicopters trying to reach people stuck on what was left of their homes. Meanwhile, family members tried to locate missing loved ones, and survivors recounted harrowing escapes. Leandra Johnson, 35, said she awoke to a frantic call at 3:28 a.m. from her aunt, who warned that she should leave her home immediately. Johnson, her husband, their 15-year-old son and 14-year-old daughter placed their small daschund-Chihuahua-mix dog in a carrier and put a leash on their Saint Berdoodle and headed out into the dark. “It was pitch-black dark,” she said. “I don’t even think my shoes matched. I just knew that if we don’t get out of here, we’re going to die.” The family waded through water, climbed over debris and slid through mud for about two miles before they met up with Johnson’s father, who then drove them to his home. “When I saw my dad, I just felt so at ease,” she said. “I just felt safe.”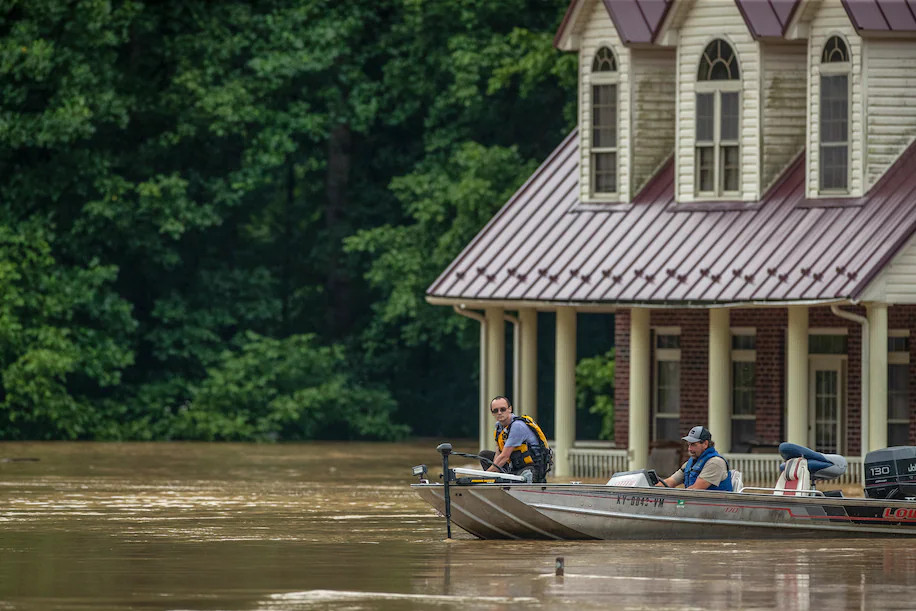 
Homes are flooded near Lost Creek, Ky., on July 28. (Ryan C. Hermens/Lexington Herald-Leader/AP) The flooding comes seven months after dozens were killed in Kentucky when tornadoes tore through a swath of the South and the Midwest. The heavy rainfall was spawned by the same stalled weather front that caused historic flooding in St. Louis on Tuesday. The deluges in St. Louis and eastern Kentucky are both considered events with less than a 1-in-1,000 chance of occurring in a given year. Flash flooding began Wednesday night after afternoon storms that evolved into a raging deluge. Like train cars along a track, storms passed over the same areas repeatedly. The storm front developed along the northern periphery of a tropical heat dome that sprawled over much of the southern United States. The extreme rainfall triggered three flash flood emergencies, each issued by the Weather Service office in Jackson, about 155 miles southeast of Louisville. Reserved for the worst flooding situations, these emergencies are sparingly issued and indicate that life-threatening flash flooding is occurring. The city of Hazard was among the hardest-hit, with at least 9 inches of rain falling in 12 hours Wednesday night into Thursday morning. Similar amounts fell around Jackson. Flooding also was widespread in Southwest Virginia, where water entered homes and roads, forcing evacuations and rescues. The extreme weather hit just two weeks after devastating flooding in Buchanan County in southwest Virginia. Historic flooding in St. Louis kills at least 1, strands others In addition to dozens of flooded houses and businesses in Kentucky, about 25,000 customers were without power because of the severe weather. Scott Sandlin, answering phones for the Perry County Emergency Management Agency, said he has lived in the county for 57 years and anticipated “massive property damage.” He said the office has received about 200 calls from people trapped in their home and in the mountains. Bridges have washed away. “Our county has been devastated. We’ve just washed away,” Scott said. “It’s been the highest level of water I’ve ever seen.” 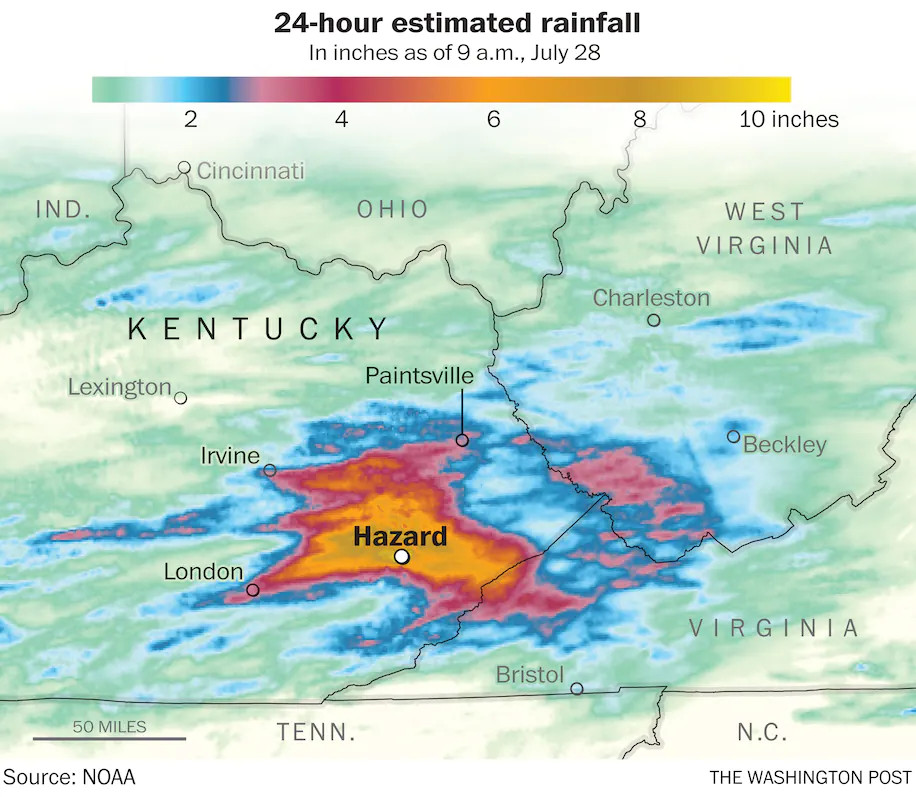
Johnson and her husband were able to assess the damage to their own property through home security cameras once daylight came. She saw a refrigerator float across the family’s front yard and the crawl space where they store canned green beans and homemade pickles destroyed. But it appeared that most of the house had been spared. Despite the widespread destruction, Johnson said she was comforted by the camaraderie of neighbors working together to clear roads and help those displaced. Her family got pizza for lunch from a local school. “It’s very heartwarming to see everyone coming together to help one another,” she said. “It’s going to take a long time for our community to build back from this.” Beshear issued a statewide state of emergency and activated the Kentucky National Guard to assist victims and the recovery effort Thursday morning. Additional planes were coming from West Virginia, and boats being flown in to assist those from the Kentucky Department of Fish and Wildlife Resources. Black Hawk helicopter crews are rescuing people trapped on rooftops, including at a school, said Maj. Gen. Haldane B. Lamberton, head of the state’s Army and Air National Guard, at the midday news conference Thursday. The region where flooding is most widespread is mountainous, the downpours magnified by the terrain, which funnels water into valley towns below. In many spots, trickling streams turned into raging rivers within a few hours, allowing little time for escape. Rockslides and mudslides also have been reported, some of which have cut off communities. Extreme levels of atmospheric moisture fed rainfall totals, which were “more than double (!) the 1-in-100 average annual chance threshold, and a couple inches beyond even the 1-in-1000 threshold,” National Weather Service meteorologist Alex Lamers tweeted. Wednesday became Jackson’s second-wettest day on record, with 4.11 inches; additional rain fell into Thursday morning.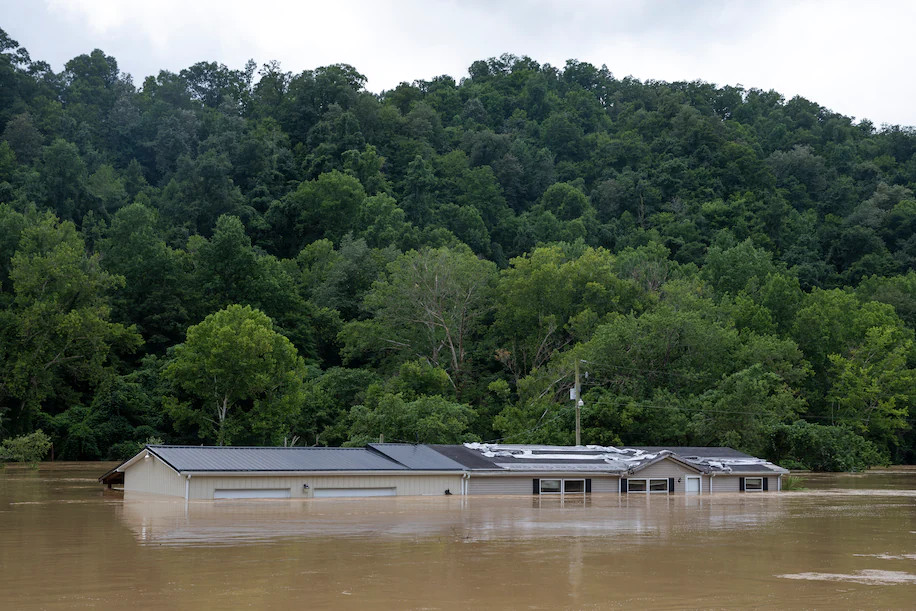 
A home sits almost completely submerged along KY-15. (Arden S. Barnes for The Washington Post) Some of the top rainfall totals reported in Kentucky include Buckhorn Lake, with 10.40 inches, and Pippa Passes, with 9.27 inches. Higher amounts probably occurred, with radar estimates as high as 11 inches. The total at Buckhorn Lake was very close to the 24-hour state record for Kentucky of 10.48 inches. The north fork of the Kentucky River shattered its record crest. Rising to over 20 feet on Thursday morning, it easily moved past the record mark of 14.7 feet from 1957. The river level shot up 17 feet in less than 12 hours. River crests may not yet have occurred in some locations as water continues to move out of the mountains and downstream. 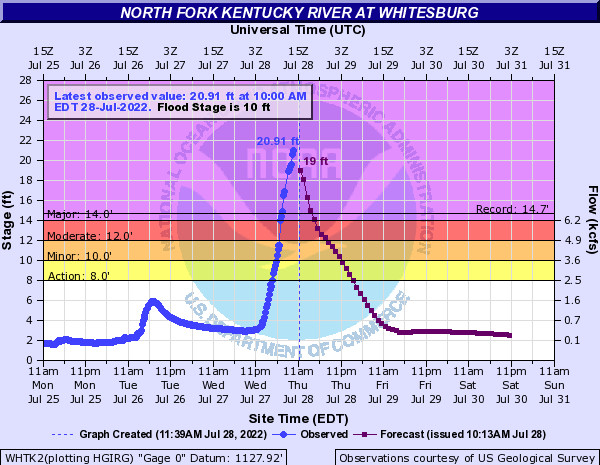
(National Weather Service) Extreme precipitation events, tied to human-induced climate change, have increased dramatically over the past 100 years. The U.S. government’s National Climate Assessment shows that heavy rainfall is now about 20 to 40 percent more likely in and around eastern Kentucky than it was around 1900. New rounds of heavy rain are likely through Friday. The Weather Service has placed eastern Kentucky and western West Virginia under a Level 3 of 4 moderate risk for excessive rainfall. Forecasters were expecting 1 to 3 additional inches Thursday and rainfall rates as high as 2 to 3 inches per hour Friday. In addition to ongoing flood warnings, a flood watch remains in effect until late Friday for much of eastern Kentucky, Southwest Virginia and southern West Virginia. By Saturday, the front responsible for the flooding is likely to move south of the region, which should lower the threat of flooding significantly. The displaced began arriving Thursday afternoon at a local community college in Jackson. Tired and anxious, they rested on rows of green cots with bags of belongings and pets nearby.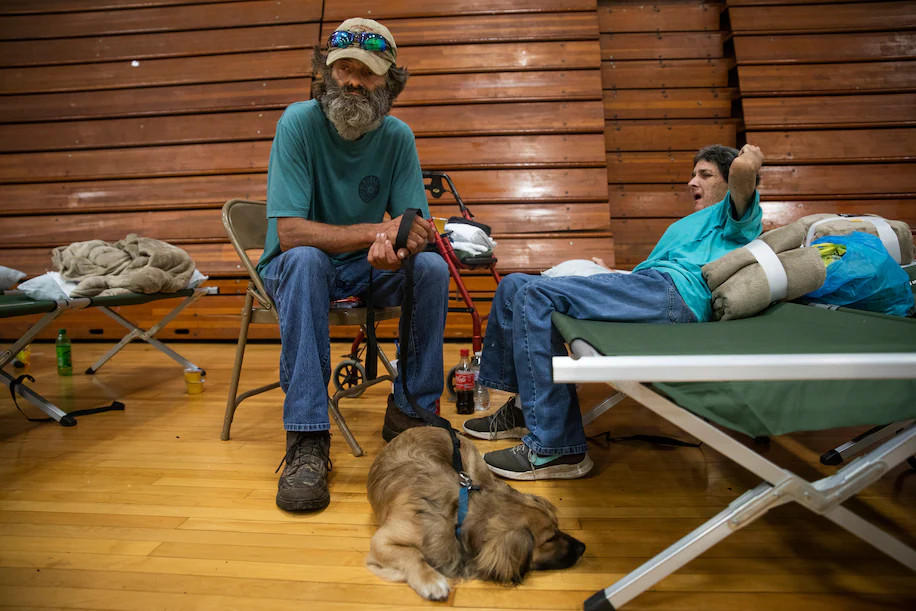 
Robert Hollan, Kimberly DiVietri and their dog, Rascal, wait in a shelter at a community college in Jackson on July 28. (Arden S. Barnes for The Washington Post) Closer to the damage, Lesia Watkins stood and watched on a slightly elevated portion of road as murky brown floodwaters swirled around her family’s home on the banks of the north fork of the Kentucky River near Jackson. As neighbors waded through waist-deep water nearby, Watkins said she hadn’t yet stepped in the water to test the depth around her house, but the lifelong Breathitt County resident added that it was the highest she had ever seen. The water was level with Watkins’s front porch. “Love your loved ones a little tighter,” Watkins said. “Hug them a little tighter. Don’t take a day for granted. Don’t take nothing for granted.” Watkins said she and her husband had been up all of the previous night as rain pounded the area. By about 3 a.m., they had lost cell service. They have multiple friends that they haven’t been able to make contact with and are “basically missing.” “We have a friend who’s got a set of twins and a smaller child,” Watkins said. “Nobody has been able to make contact with her. She was stranded. She had no way of getting out.” With 1 to 3 more inches of rain forecast for Thursday night into Friday, Watkins said they’ll just have to “wait and see.” “I’m just wondering if I’ll have a home tomorrow or not,” she said.
FLOODING DISASTERS AND SAFETY Do you need special flood and sewer insurance? Here’s how to tell. News• April 20, 2022 5 things you need to do the day after a basement flood News• September 2, 2021 Tens of millions of people have been moving into flood zones, satellite imagery shows News• August 4, 2021
| The text being discussed is available at | https://www.washingtonpost.com/climate-environment/2022/07/28/kentucky-flooding-jackson-hazard/ and |